Detailed information of T6SS
Note: only experimentally validated proteins are displayed in the graph.
Summary
| T6SS ID | T6SS00003 |
| T6SS type | Type i3 |
| Strain | Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 |
| Replicon (RefSeq) | chromosome (H1-T6SS) (NC_002516) |
| Location | 83380..123495 |
| Function | anti-bacterial; anti-eukaryotic; effector translocation; virulence |
| Comment | Virulence in rat model of chronic respiratory infection; Ability to outcompete a susceptible mutant of P. aeruginosa; ability to outcompete P. putida; growth inhibition of E. coli. |
| References | [1] Zou T et al (2012) Crystal structure of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Tsi2 reveals a stably folded superhelical antitoxin. J Mol Biol. 417(4):351-61. [PudMed:22310046] [2] Silverman JM et al (2011) Separate inputs modulate phosphorylation-dependent and -independent type VI secretion activation. Mol Microbiol. 82(5):1277-90. [PudMed:22017253] [3] Hachani A et al (2014) The VgrG proteins are "A la carte" delivery systems for bacterial type VI effectors. J Biol Chem. 289(25):17872-17884. [PudMed:24794869] [4] Osipiuk J et al (2011) Crystal structure of secretory protein Hcp3 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Struct Funct Genomics. 12(1):21-6. [PudMed:21476004] [5] Hsu F et al (2009) TagR promotes PpkA-catalysed type VI secretion activation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Microbiol. 72(5):1111-25. [PudMed:19400797] [6] Leroux M et al (2012) Quantitative single-cell characterization of bacterial interactions reveals type VI secretion is a double-edged sword. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 109(48):19804-9. [PudMed:23150540] [7] Li M et al (2012) Structural basis for type VI secretion effector recognition by a cognate immunity protein. PLoS Pathog. 8(4):e1002613. [PudMed:22511866] [8] Mougous JD et al (2007) Threonine phosphorylation post-translationally regulates protein secretion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nat Cell Biol. 9(7):797-803. [PudMed:17558395] [9] Kefala K et al (2012) Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of the C-terminal fragment of the MvfR protein from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 68(Pt 6):695-7. [PudMed:22684073] [10] Lossi NS et al (2012) The archetype Pseudomonas aeruginosa proteins TssB and TagJ form a novel subcomplex in the bacterial type VI secretion system. Mol Microbiol. 86(2):437-56. [PudMed:22906320] [11] Sana TG et al (2012) The Second Type VI Secretion System of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strain PAO1 Is Regulated by Quorum Sensing and Fur and Modulates Internalization in Epithelial Cells. J Biol Chem. 287(32):27095-105. [PudMed:22665491] [12] Lu D et al (2013) Expression, purification and preliminary crystallographic analysis of the T6SS effector protein Tse3 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 69(Pt 5):524-7. [PudMed:23695568] [13] Ding J et al (2012) Structural Insights into the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Type VI Virulence Effector Tse1 Bacteriolysis and Self-protection Mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 287(32):26911-20. [PudMed:22700987] [14] Bleves S et al (2010) Protein secretion systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A wealth of pathogenic weapons. Int J Med Microbiol. 300(8):534-43. [PudMed:20947426] [15] Robb CS et al (2013) Structure of the T6SS lipoprotein TssJ1 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 69(Pt 6):607-10. [PudMed:23722835] [16] Forster A et al (2014) Coevolution of the ATPase ClpV, the Sheath Proteins TssB and TssC and the Accessory Protein TagJ/HsiE1 Distinguishes Type VI Secretion Classes. J Biol Chem. 289(47):33032-43. [PudMed:25305017] [17] Chou S et al (2012) Structure of a Peptidoglycan Amidase Effector Targeted to Gram-Negative Bacteria by the Type VI Secretion System. Cell Rep. 1(6):656-64. [PudMed:22813741] [18] Zhang H et al (2012) Crystal structure of type VI effector Tse1 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEBS Lett. 586(19):3193-9. [PudMed:22750141] [19] Hood RD et al (2010) A type VI secretion system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa targets a toxin to bacteria. Cell Host Microbe. 7(1):25-37. [PudMed:20114026] [20] Basler M et al (2013) Tit-for-Tat: Type VI Secretion System Counterattack during Bacterial Cell-Cell Interactions. Cell. 152(4):884-94. [PudMed:23415234] [21] Russell AB et al (2011) Type VI secretion delivers bacteriolytic effectors to target cells. Nature. 475(7356):343-7. [PudMed:21776080] [22] Whitney JC et al (2014) Genetically distinct pathways guide effector export through the type VI secretion system. Mol Microbiol. 92(3):529-42. [PudMed:24589350] [23] Casabona MG et al (2012) An ABC transporter and an outer membrane lipoprotein participate in posttranslational activation of type VI secretion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Environ Microbiol. 15(2):471-86. [PudMed:22765374] [24] Goldova J et al (2011) A eukaryotic-type signalling system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa contributes to oxidative stress resistance, intracellular survival and virulence. BMC Genomics. 0.803472222. [PudMed:21880152] [25] Lossi NS et al (2011) Structure-function analysis of HsiF, a gp25-like component of the type VI secretion system, in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology. 157(Pt 12):3292-305. [PudMed:21873404] [26] Barret M et al (2011) Genomic analysis of the type VI secretion systems in Pseudomonas spp.: novel clusters and putative effectors uncovered. Microbiology. 157(Pt 6):1726-39. [PudMed:21474537] [27] Hachani A et al (2011) Type VI secretion system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: secretion and multimerization of VgrG proteins. J Biol Chem. 286(14):12317-27. [PudMed:21325275] [28] Mougous JD et al (2006) A virulence locus of Pseudomonas aeruginosa encodes a protein secretion apparatus. Science. 312(5779):1526-30. [PudMed:16763151] |
T6SS components and genome coordinates
| Component | FHA | PpkA | PppA | TagF | TagJ | TagQ | TagR | TagS | TagT | TssA | TssB | TssC | TssD | TssE | TssF | TssG | TssH | TssI | TssJ | TssK | TssL | TssM |
| Number | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
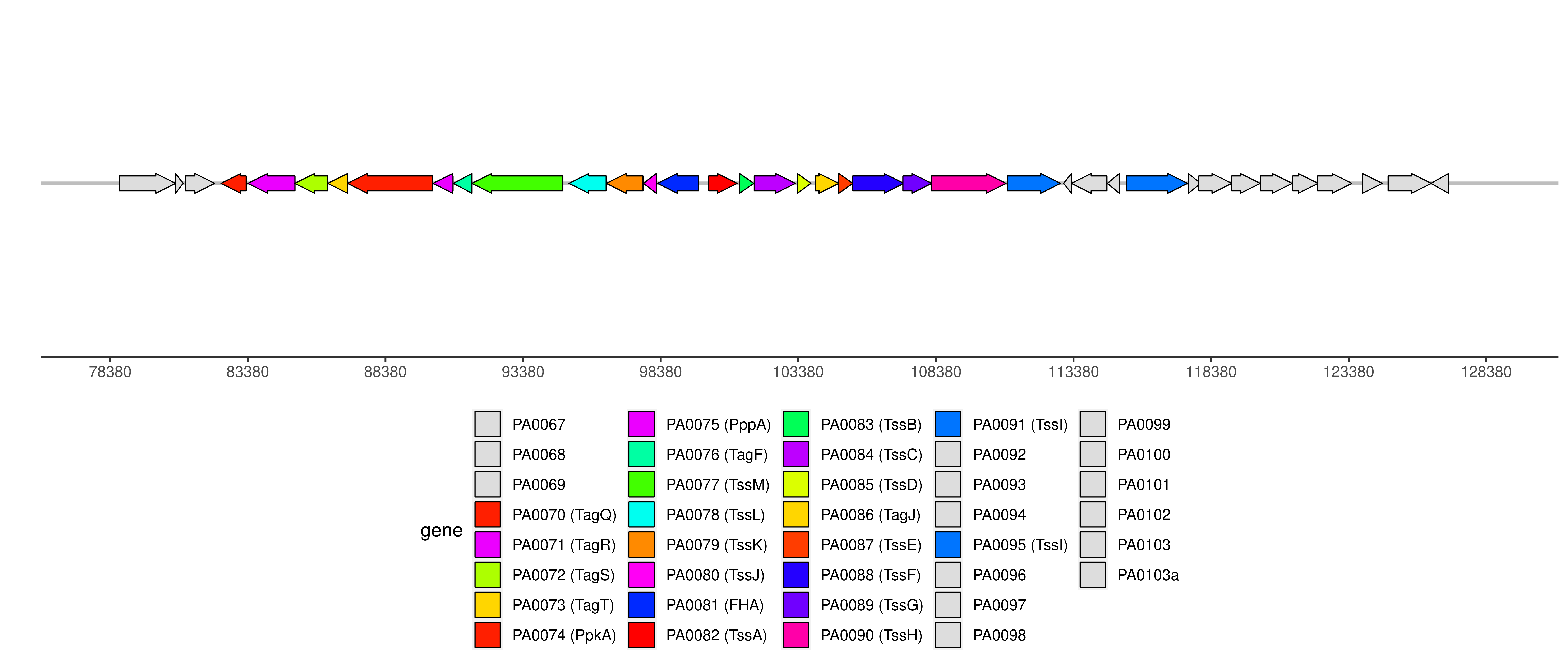
| Component ID | Component | Locus tag (Gene) | Coordinate | Strand | Size (bp) | NCBI ID | Product |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA0067 (prlC) | 78710..80755 | + | 2046 | NP_248757.1 | oligopeptidase A | ||
| PA0068 | 80752..81027 | + | 276 | NP_248758.1 | hypothetical protein | ||
| PA0069 | 81116..82174 | + | 1059 | NP_248759.1 | hypothetical protein | ||
| T6CP012414 | TagQ | PA0070 | 82404..83318 | - | 915 | NP_248760.1 | hypothetical protein |
| T6CP012415 | TagR | PA0071 | 83380..85092 | - | 1713 | NP_248761.1 | hypothetical protein |
| T6CP012416 | TagS | PA0072 | 85085..86284 | - | 1200 | NP_248762.1 | hypothetical protein |
| T6CP012417 | TagT | PA0073 | 86284..87003 | - | 720 | NP_248763.1 | ABC transporter ATP-binding protein |
| T6CP012418 | PpkA | PA0074 (ppkA) | 87000..90098 | - | 3099 | NP_248764.1 | serine/threonine protein kinase PpkA |
| T6CP012419 | PppA | PA0075 (pppA) | 90106..90834 | - | 729 | NP_248765.1 | serine/threonine phosphatase |
| T6CP012420 | TagF | PA0076 | 90844..91524 | - | 681 | NP_248766.1 | hypothetical protein |
| T6CP005094 | TssM | PA0077 (icmF1) | 91521..94826 | - | 3306 | NP_248767.1 | type VI secretion protein IcmF |
| T6CP005095 | TssL | PA0078 | 95048..96397 | - | 1350 | NP_248768.1 | hypothetical protein |
| T6CP005096 | TssK | PA0079 | 96404..97738 | - | 1335 | NP_248769.1 | hypothetical protein |
| T6CP005097 | TssJ | PA0080 | 97754..98218 | - | 465 | NP_248770.1 | hypothetical protein |
| T6CP011390 | FHA | PA0081 (fha1) | 98263..99756 | - | 1494 | NP_248771.1 | Fha domain-containing protein |
| T6CP005098 | TssA | PA0082 | 100124..101158 | + | 1035 | NP_248772.1 | hypothetical protein |
| T6CP005099 | TssB | PA0083 | 101247..101765 | + | 519 | NP_248773.1 | hypothetical protein |
| T6CP005100 | TssC | PA0084 | 101778..103274 | + | 1497 | NP_248774.1 | hypothetical protein |
| T6CP005101 | TssD | PA0085 (hcp1) | 103350..103838 | + | 489 | NP_248775.1 | protein secretion apparatus assembly protein |
| T6CP012694 | TagJ | PA0086 | 104006..104851 | + | 846 | NP_248776.1 | hypothetical protein |
| T6CP005102 | TssE | PA0087 | 104853..105362 | + | 510 | NP_248777.1 | hypothetical protein |
| T6CP005103 | TssF | PA0088 | 105359..107218 | + | 1860 | NP_248778.1 | hypothetical protein |
| T6CP005104 | TssG | PA0089 | 107182..108228 | + | 1047 | NP_248779.1 | hypothetical protein |
| T6CP005105 | TssH | PA0090 (clpV1) | 108221..110929 | + | 2709 | NP_248780.1 | secretion protein ClpV1 |
| T6CP005106 | TssI | PA0091 (vgrG1) | 110976..112907 | + | 1932 | NP_248781.1 | type VI secretion system protein VgrG |
| PA0092 | 113022..113306 | - | 285 | NP_248782.1 | hypothetical protein | ||
| PA0093 | 113303..114595 | - | 1293 | NP_248783.1 | hypothetical protein | ||
| PA0094 | 114611..115045 | - | 435 | NP_248784.1 | hypothetical protein | ||
| T6CP005107 | TssI | PA0095 | 115299..117524 | + | 2226 | NP_248785.1 | hypothetical protein |
| PA0096 | 117552..118001 | + | 450 | NP_248786.1 | hypothetical protein | ||
| PA0097 | 117931..119130 | + | 1200 | NP_248787.1 | hypothetical protein | ||
| PA0098 | 119127..120164 | + | 1038 | NP_248788.1 | 3-oxoacyl-ACP synthase | ||
| PA0099 | 120164..121324 | + | 1161 | NP_248789.1 | hypothetical protein | ||
| PA0100 | 121346..122266 | + | 921 | NP_248790.1 | hypothetical protein | ||
| PA0101 | 122248..123495 | + | 1248 | NP_248791.1 | hypothetical protein | ||
| PA0102 | 123871..124599 | + | 729 | NP_248792.1 | carbonic anhydrase | ||
| PA0103 | 124810..126381 | + | 1572 | NP_248793.1 | sulfate transporter | ||
| PA0103a | 126368..127006 | - | 639 | YP_008719730.1 | hypothetical protein |
Download FASTA format files
Note: in the 'Target' column, ↓ means the target is positively regulated by the regulator, while ↑ indicates negatively regulation.
| Accessory protein ID | Locus tag (Gene) | Type | Organism | Replicon (Accession) | Coordinates (Strand) | NCBI ID | Related structure protein | Related effector |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACP00002 |
PA0094 (eagT6) | adaptor | Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 | chromosome (NC_002516) | 114611..115045 (-) | 15595292 | - | PA0093 (Tse6) |
| ACP00003 |
PA0086 (tagJ) | structure affiliated protein | Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 | chromosome (NC_002516) | 104006..104851 (+) | 15595284 | PA0082 (TssA) | - |
| ACP00004 |
PA0086 (tagJ) | structure affiliated protein | Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 | chromosome (NC_002516) | 104006..104851 (+) | 15595284 | PA0083 (HisB1/TssB1) | - |