
| 19 | |
| Agrobacterium tumefaciens str. C58 | |
| plasmid Ti [Browse all T4SS(s) in this replicon] | |
| NC_003065 | |
| 183877..201962 | |
| VirB | |
| effector translocation and conjugation | |
| Type IVA; Type P | |
T4SS components |
| Component | VirB1 | VirB2 | VirB3 | VirB4 | VirB5 | VirB6 | VirB7 | VirB8 | VirB9 |
| Number | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Component | VirB10 | VirB11 | VirD4 | ||||||
| Number | 1 | 1 | 1 |
The information of T4SS components from NC_003065 | ||||||
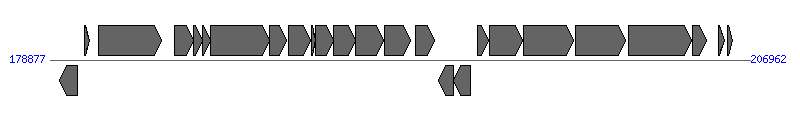 | ||||||
| # | Locus tag (Gene) | Coordinates [+/-], size (bp) | Protein GI | Product | Component | |
| 1 | Atu6164 (tzs) | 179262..179993 [-], 732 | 41223351 | trans-zeatin secretion protein | ||
| 2 | Atu6165 | 180279..180470 [+], 192 | 159161997 | hypothetical protein | ||
| 3 | Atu6166 (virA) | 180831..183332 [+], 2502 | 16119781 | two-component VirA-like sensor kinase | ||
| 4 | Atu6167 (virB1) | 183877..184614 [+], 738 | 41223307 | type IV secretion system lytic transglycosylase VirB1 | VirB1 | |
| 5 | Atu6168 (virB2) | 184614..184979 [+], 366 | 16119783 | type IV secretion system pilin subunit VirB2 | VirB2 | |
| 6 | Atu6169 (virB3) | 184979..185305 [+], 327 | 16119784 | type IV secretion system protein VirB3 | VirB3 | |
| 7 | Atu6170 (virB4) | 185305..187674 [+], 2370 | 16119786 | type IV secretion system protein VirB4 | VirB4 | |
| 8 | Atu6171 (virB5) | 187691..188353 [+], 663 | 16119787 | type IV secretion system protein VirB5 | VirB5 | |
| 9 | Atu6172 (virB6) | 188454..189341 [+], 888 | 41223308 | type IV secretion system protein VirB6 | VirB6 | |
| 10 | Atu6173 (virB7) | 189377..189544 [+], 168 | 159161998 | type IV secretion system lipoprotein VirB7 | VirB7 | |
| 11 | Atu6174 (virB8) | 189531..190244 [+], 714 | 41223309 | type IV secretion system protein VirB8 | VirB8 | |
| 12 | Atu6175 (virB9) | 190241..191122 [+], 882 | 16119791 | type IV secretion system protein VirB9 | VirB9 | |
| 13 | Atu6176 (virB10) | 191119..192252 [+], 1134 | 16119792 | type IV secretion system protein VirB10 | VirB10 | |
| 14 | Atu6177 (virB11) | 192293..193327 [+], 1035 | 41223310 | type IV secretion system protein VirB11 | VirB11 | |
| 15 | Atu6178 (virG) | 193546..194307 [+], 762 | 16119794 | two-component response regulator VirG | ||
| 16 | Atu6179 (virC2) | 194449..195057 [-], 609 | 159161999 | putative crown gall tumor protein VirC2 | ||
| 17 | Atu6180 (virC1) | 195060..195755 [-], 696 | 16119796 | putative crown gall tumor protein VirC1 | ||
| 18 | Atu6181 (virD1) | 196026..196469 [+], 444 | 41223311 | type IV secretion system T-DNA border endonuclease VirD1 | ||
| 19 | Atu6182 (virD2) | 196503..197846 [+], 1344 | 16119798 | type IV secretion system T-DNA border endonuclease VirD2 | ||
| 20 | Atu6183 (virD3) | 197861..199882 [+], 2022 | 159162000 | virA/G regulated protein | ||
| 21 | Atu6184 (virD4) | 199956..201962 [+], 2007 | 41223312 | type IV secretion system protein VirD4 | VirD4 | |
| 22 | Atu6185 (virD5) | 202074..204596 [+], 2523 | 16119801 | virA/G regulated protein | ||
| 23 | Atu6186 (virE3) | 204666..205232 [+], 567 | 159162001 | virA/G regulated protein | ||
| 24 | Atu6188 (virE0) | 205684..205935 [+], 252 | 159162002 | virA/G regulated protein | ||
| 25 | Atu6189 (virE1) | 206051..206242 [+], 192 | 16119804 | type IV secretion system chaperone VirE1 | ||
Download FASTA format files |
| Proteins Genes |
| This system delivers both oncogenic DNA and proteins into plant cells. The transferred DNA (T-DNA, NC_003065 REGION: 1..24836) is processed by VirD1, VirD2, and VirC1 (Dtr proteins) and covalently bound to VirD2 to form a VirD2-T-strand transfer intermediate. The T-DNA complex is then transferred by this system into target cells. In addition, the T4SS independently translocates four additional effector proteins: VirE2, VirE3, VirF and VirD5. |
Effectors |
| VirD2, VirD5, VirE2, VirE3, VirF |
The information of protein effectors | ||||||
| # | Locus tag (Gene) | Coordinates [+/-], size (bp) | Protein GI | Product | * | |
| 1 | Atu6182 (virD2) | 196503..197846 [+], 1344 | 16119798 | type IV secretion system T-DNA border endonuclease VirD2 | ||
| 2 | Atu6185 (virD5) | 202074..204596 [+], 2523 | 16119801 | virA/G regulated protein | ||
| 3 | Atu6190 (virE2) | 206256..207926 [+], 1671 | 16119805 | type IV secretion system single-stranded DNA binding protein VirE2 | ||
| 4 | Atu6191 (virE3) | 207993..210047 [+], 2055 | 16119806 | virA/G regulated protein | ||
| 5 | Atu6154 (virF) | 172489..173427 [+], 939 | 16119971 | exported virulence protein | ||
Download FASTA format files |
| Proteins Genes |
| # | Name | Image | Resource | Detail | Reference |
| 1 | VirB8 | 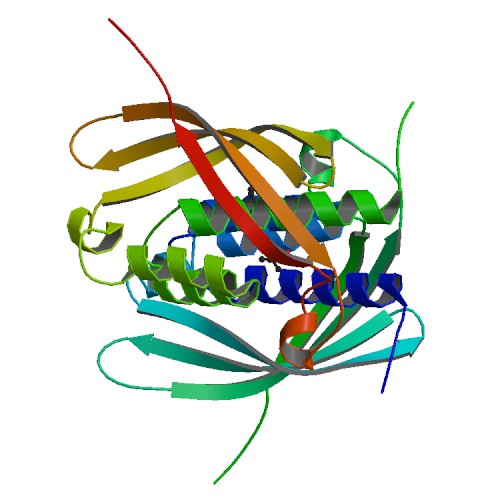 | PDB (2CC3) | Structure of Agrobacterium tumefaciens VirB8 protein | (1) PubMed: 16481621 |
|
(1) Bailey S; Ward D; Middleton R; Grossmann JG; Zambryski PC (2006). Agrobacterium tumefaciens VirB8 structure reveals potential protein-protein interaction sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 103(8):2582-7. [PudMed:16481621] |
| # | Accessory protein(GI) | motif(s) | Substrate(s) | Function | Reference |
| 1 | VirC1 (16119796) | ND | VirD2 | VirC1 pairwise interacts with the processing factors VirD2 relaxase, VirC2, and VirD1 to stimulate generation of multiple copies per cell of the T-DNA substrate. VirC1 promotes conjugative T-DNA transfer. | (1) PubMed: 17505518 |
| 2 | VirE1 chaperone (16119804) | CT50aa sufficient (interacts with the VirD4 T4CP. CT100aa(VirE2) sufficient for the T4CP interation) | VirE2 | Translocation of the VirE2 effector through the A. tumefaciens VirB/VirD4 T4SS requires VirE1. | (2) PubMed: 19946141 |
|
(1) Atmakuri K; Cascales E; Burton OT; Banta LM; Christie PJ (2007). Agrobacterium ParA/MinD-like VirC1 spatially coordinates early conjugative DNA transfer reactions. EMBO J. 26(10):2540-51. [PudMed:17505518] |
| (2) Alvarez-Martinez CE; Christie PJ (2009). Biological diversity of prokaryotic type IV secretion systems. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 73(4):775-808. [PudMed:19946141] |
|
(1) Aguilar J; Cameron TA; Zupan J; Zambryski P (2011). Membrane and core periplasmic Agrobacterium tumefaciens virulence Type IV secretion system components localize to multiple sites around the bacterial perimeter during lateral attachment to plant cells. MBio. 2(6):e00218-11. [PudMed:22027007] |
|
(2) Sivanesan D; Baron C (2011). The dimer interface of Agrobacterium tumefaciens VirB8 is important for type IV secretion system function, stability, and association of VirB2 with the core complex. J Bacteriol. 193(9):2097-106. [PudMed:21398549] |
|
(3) Mossey P; Hudacek A; Das A (2010). Agrobacterium tumefaciens type IV secretion protein VirB3 is an inner membrane protein and requires VirB4, VirB7, and VirB8 for stabilization. J Bacteriol. 192(11):2830-8. [PudMed:20348257] |
|
(4) Aguilar J; Zupan J; Cameron TA; Zambryski PC (2010). Agrobacterium type IV secretion system and its substrates form helical arrays around the circumference of virulence-induced cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 107(8):3758-63. [PudMed:20133577] |
|
(5) Zupan J; Hackworth CA; Aguilar J; Ward D; Zambryski P (2007). VirB1* promotes T-pilus formation in the vir-Type IV secretion system of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 189(18):6551-63. [PudMed:17631630] |
|
(6) Draper O; Middleton R; Doucleff M; Zambryski PC (2006). Topology of the VirB4 C terminus in the Agrobacterium tumefaciens VirB/D4 type IV secretion system. J Biol Chem. 281(49):37628-35. [PudMed:17038312] |
|
(7) Wessel M; Klusener S; Godeke J; Fritz C; Hacker S; Narberhaus F (2006). Virulence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens requires phosphatidylcholine in the bacterial membrane. Mol Microbiol. 62(3):906-15. [PudMed:17010159] |
| (8) McCullen CA; Binns AN (2006). Agrobacterium tumefaciens and plant cell interactions and activities required for interkingdom macromolecular transfer. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 22:101-27. [PudMed:16709150] |
|
(9) Bailey S; Ward D; Middleton R; Grossmann JG; Zambryski PC (2006). Agrobacterium tumefaciens VirB8 structure reveals potential protein-protein interaction sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 103(8):2582-7. [PudMed:16481621] |
|
(10) Middleton R; Sjolander K; Krishnamurthy N; Foley J; Zambryski P (2005). Predicted hexameric structure of the Agrobacterium VirB4 C terminus suggests VirB4 acts as a docking site during type IV secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 102(5):1685-90. [PudMed:15668378] |
|
(11) Ward DV; Draper O; Zupan JR; Zambryski PC (2002). Peptide linkage mapping of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens vir-encoded type IV secretion system reveals protein subassemblies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 99(17):11493-500. [PudMed:12177441] |
|
(12) Hapfelmeier S; Domke N; Zambryski PC; Baron C (2000). VirB6 is required for stabilization of VirB5 and VirB3 and formation of VirB7 homodimers in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 182(16):4505-11. [PudMed:10913084] |