
| 35 | |
| Helicobacter pylori P12 | |
| chromosome [Browse all T4SS(s) in this replicon] | |
| NC_011498 | |
| 553525..584777 | |
| Cag | |
| effector translocation | |
| Type IVA; Type P | |
T4SS components |
| Component | CagC | CagD | CagE | CagF | CagG | CagH | CagI | CagL | CagN |
| Number | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Component | CagM | CagT | CagU | CagV | CagW | CagX | CagY | CagZ | Cagalpha |
| Number | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Component | Cagbeta | Caggamma | Cagdelta | ||||||
| Number | 1 | 1 | 1 |
The information of T4SS components from NC_011498 | ||||||
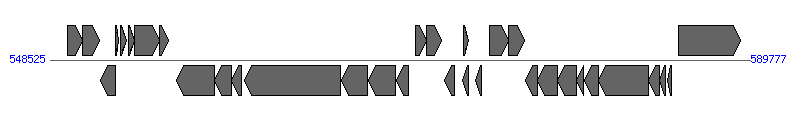 | ||||||
| # | Locus tag (Gene) | Coordinates [+/-], size (bp) | Protein GI | Product | Component | |
| 1 | HPP12_0523 (era) | 549537..550442 [+], 906 | 210134718 | GTP-binding protein Era | ||
| 2 | HPP12_0524 | 550439..551431 [+], 993 | 210134719 | hypothetical protein | ||
| 3 | HPP12_0525 | 551520..552374 [-], 855 | 210134720 | hypothetical protein | ||
| 4 | HPP12_0526 | 552393..552584 [+], 192 | 210134721 | hypothetical protein | ||
| 5 | HPP12_0527 (cag1) | 552705..553052 [+], 348 | 210134722 | cag pathogenicity island protein Zeta | ||
| 6 | HPP12_0528 (cag2) | 553160..553525 [+], 366 | 210134723 | cag pathogenicity island protein Epsilon | ||
| 7 | HPP12_0529 (cag3) | 553525..554970 [+], 1446 | 210134724 | cag pathogenicity island protein Delta | Cagdelta | |
| 8 | HPP12_0530 (cag4) | 554980..555489 [+], 510 | 210134725 | cag pathogenicity island protein Gamma | Caggamma | |
| 9 | HPP12_0531 (cag5) | 555963..558209 [-], 2247 | 210134726 | cag pathogenicity island protein Beta | Cagbeta | |
| 10 | HPP12_0532 (virB11-2) | 558218..559210 [-], 993 | 210134727 | cag pathogenicity island protein Alpha | Cagalpha | |
| 11 | HPP12_0533 (cagZ) | 559215..559814 [-], 600 | 210134728 | cag pathogenicity island protein Z | CagZ | |
| 12 | HPP12_0534 (cagY) | 559964..565669 [-], 5706 | 210134729 | cag pathogenicity island protein Y VirB10-like protein | CagY | |
| 13 | HPP12_0535 (cagX) | 565684..567252 [-], 1569 | 210134730 | cag pathogenicity island protein X VirB9-like protein | CagX | |
| 14 | HPP12_0536 (cagW) | 567305..568912 [-], 1608 | 210134731 | cag pathogenicity island protein W | CagW | |
| 15 | HPP12_0537 (cagV) | 568917..569675 [-], 759 | 210134732 | cag pathogenicity island protein V | CagV | |
| 16 | HPP12_0538 (cagU) | 570070..570720 [+], 651 | 210134733 | cag pathogenicity island protein U | CagU | |
| 17 | HPP12_0539 (cagT) | 570733..571575 [+], 843 | 210134734 | cag pathogenicity island protein T | CagT | |
| 18 | HPP12_0540 (cagS) | 571777..572376 [-], 600 | 210134735 | cag pathogenicity island protein S | ||
| 19 | HPP12_0541 (cagQ) | 572815..573195 [-], 381 | 210134736 | cag pathogenicity island protein Q | ||
| 20 | HPP12_0542 (cagR) | 572903..573205 [+], 303 | 210134737 | cag pathogenicity island protein R | ||
| 21 | HPP12_0543 (cagP) | 573621..573974 [-], 354 | 210134738 | cag pathogenicity island protein P | ||
| 22 | HPP12_0544 (cagM) | 574409..575539 [+], 1131 | 210134739 | cag pathogenicity island protein M | CagM | |
| 23 | HPP12_0545 (cagN) | 575554..576474 [+], 921 | 210134740 | cag pathogenicity island protein N | CagN | |
| 24 | HPP12_0546 (cagL) | 576555..577268 [-], 714 | 210134741 | cag pathogenicity island protein L | CagL | |
| 25 | HPP12_0547 (cagI) | 577265..578410 [-], 1146 | 210134742 | cag pathogenicity island protein I | CagI | |
| 26 | HPP12_0548 (cagH) | 578421..579533 [-], 1113 | 210134743 | cag pathogenicity island protein H | CagH | |
| 27 | HPP12_0549 (cagG) | 579550..579978 [-], 429 | 210134744 | cag pathogenicity island protein G | CagG | |
| 28 | HPP12_0550 (cagF) | 580037..580843 [-], 807 | 210134745 | cag pathogenicity island protein F | CagF | |
| 29 | HPP12_0551 (cagE) | 580845..583796 [-], 2952 | 210134746 | cag pathogenicity island protein E VirB4-like protein | CagE | |
| 30 | HPP12_0552 (cagD) | 583805..584428 [-], 624 | 210134747 | cag pathogenicity island protein D | CagD | |
| 31 | HPP12_0553 (cagC) | 584430..584777 [-], 348 | 210134748 | cag pathogenicity island protein C | CagC | |
| 32 | HPP12_0554 (cagB) | 584923..585150 [-], 228 | 210134749 | cag pathogenicity island protein B | ||
| 33 | HPP12_0555 (cagA) | 585581..589225 [+], 3645 | 210134750 | cytotoxin-associated protein A | ||
Download FASTA format files |
| Proteins Genes |
Effectors |
| CagA; Peptidoglycan |
The information of protein effectors | ||||||
| # | Locus tag (Gene) | Coordinates [+/-], size (bp) | Protein GI | Product | * | |
| 1 | HPP12_0555 (cagA) | 585581..589225 [+], 3645 | 210134750 | cytotoxin-associated protein A | ||
Download FASTA format files |
| Proteins Genes |
| # | Accessory protein(GI) | motif(s) | Substrate(s) | Function | Reference |
| 1 | CagF (chaperone) (210134745) | CT20aa and an intact N terminus | CagA | The CagA-binding protein CagF is a secretion chaperone-like protein that interacts with a 100 aa region that is adjacent to the C-terminal secretion signal of CagA.CagF is a translocation factor for CagA, but is not translocated by the type IV apparatus. | (1) PubMed: 17768234 |
|
(1) Pattis I; Weiss E; Laugks R; Haas R; Fischer W (2007). The Helicobacter pylori CagF protein is a type IV secretion chaperone-like molecule that binds close to the C-terminal secretion signal of the CagA effector protein. Microbiology. 153(Pt 9):2896-909. [PudMed:17768234] |
| # | Name(Protein GI) | Host site/Substrate | Source | Function | Reference | |
| 1 | CagA (210134750) | SHP-2 | human | CagA is translocated into gastric epithelial cells. It physically interacts with SHP-2 to modify cellular functions and perturb mammalian signal transduction machineries. This may induce gastric epithelial cells to move and proliferate abnormally and help to acquire a cellular transformed phenotype. | (1) PubMed: 11743164 | |
| 2 | CagA (210134750) | growth factor receptor bound 2 (Grb2) | unknown | CagA targets to Grb2 and this process leads to activing the MEK/ERK pathway and results in cell scattering and proliferation. | (2) PubMed: 12419219 | |
| 3 | CagA (210134750) | PAR1/MARK kinase | human | CagA interacts with PAR1/MARK kinase to inhibit the activity of PAR1 kinase and prevent PAR1 phosphorylation which mediated by atypical protein kinase C (aPKC). | (3) PubMed: 17507984 | |
| 4 | CagA (210134750) | Apoptosis-stimulating of p53 protein 2 (ASPP2) | human | ASPP2 is a tumor suppressor that activates the apoptotic response upon cellular stress which mediated by p53. CagA interacts with ASPP2 to change the function of ASPP2 and this process leads to the decreased survival of cells which infected by H. pylori. | (4) PubMed: 24474782 | |
| 5 | CagA (210134750) | protein kinase C-related kinase 2 (PRK2) | human | CagA represses kinase activity of PRK2, which has been involved in establishment of cell polarity and rearrangements of cytoskeleton, to further control signalling pathways associated with cancer. | (5) PubMed: 26041307 | |
| 6 | CagA (210134750) | Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) | human | CagA interacts with GSK-3 to reduce its activity by cause it to transform into an insoluble fraction. CagA then induce a epithelial mesenchymal transition mediated by Snail via the comsuming of GSK-3. | (6) PubMed: 25055241 | |
| 7 | CagA (210134750) | c-Met | human | CagA interacts with the c-Met receptor to modulates cellular functions through deregulating c-Met receptor signaling and participates in invasive growth of tumor cells. | (7) PubMed: 12719469 | |
| 8 | CagA (210134750) | E-cadherin | human | CagA interacts with E-cadherin to impair the complex formation between E-cadherin and beta-catenin and facilitate transdifferentiation of intestines in gastric epithelial cells. | (8) PubMed: 17237808 | |
| 9 | CagA (210134750) | host membrane phosphatidylserine | unknown | CagA can be tethered to the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane by interacting with phosphatidylserine. Then it binds the PAR1/MARK to induce polarity and junctional defects. | (9) PubMed: 20478541 | |
| 10 | CagA (210134750) | c-Abl tyrosine kinase | human | CagA targets to c-Abl directly and localizes in focal adhesion complexes and membrane ruffles. | (10) PubMed: 17160020 | |
| 11 | CagA (210134750) | αPix | human | CagA interacted with αPix to activates PAK1, ERK and NF-kappaB after being delivered into AGS cells. Then it induces the expression of IL-8 in infected gastric epithelial cells. | (11) PubMed: 19672789 | |
| 12 | CagA (210134750) | scaffolding protein ZO-1 | human, canine | CagA interacts with epithelial tight-junction ZO-1 and the transmembrane protein junctional adhesion molecule to change the function and composition of the apical-junctional complex. | (12) PubMed: 12775840 | |
| 13 | CagA (210134750) | integrin α5β1 receptor | human | CagA binds interface with α5β1 integrin.It is an essential step for the translocation process of CagA into the host cell. | (13) PubMed: 22908298 | |
| 14 | CagA (210134750) | TNF receptor-associated factor 1 and 4-1BB (TRAF1 and 4-1BB) | human | CagA facilitates the proliferation and represses the apoptosis of GES-1 cells by upregulated TRAF1/4-1BB. | (14) PubMed: 28627614 | |
| 15 | CagA (210134750) | Adapter molecule crk | human | The interaction between CagA and Crk adaptor proteins is important for loss of gastric epithelial cell adhesion induced by Helicobacter pylori-induced Helicobacter pylori. | (15) PubMed: 16275761 | |
| 16 | CagA (210134750) | SHP-1 | human | CagA interacts with SHP1 to enhance the phosphatase activity of SHP1 so that it dampens the oncogenic action of CagA. | (16) PubMed: 27572445 | |
| 17 | CagA (210134750) | Transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) | human | CagA interacts with TAK1 and improves its activity to activate NF-kappaB through the ubiquitination of TAK1. | (17) PubMed: 19820695 | |
| 18 | CagA (210134750) | Myeloid cell leukemia sequence-1 (MCL1) | mongolian gerbil | CagA increases MCL1 thorough the interaction between SRE/SRF and CagA/MCL1 in modulating rapid turnover of pit epithelial cells via MEK/ERK/SRE activation. | (18) PubMed: 18005743 | |
| 19 | CagL (210134741) | integrin α5β1 receptor | human | CagL, which is targeted to the pilus surface, is a specialized adhesin. It binds to and activates integrin α5β1 receptor on gastric epithelial cells. This interaction triggers CagA delivery into target cells. | (19) PubMed: 17943123 | |
| 20 | CagL (210134741) | integrin αvβ3 | human | Host cell docking of T4SS. | (20) PubMed: 21915696 | |
| 21 | CagL (210134741) | integrin αvβ5 | human | CagL/integrin β5 signalling complex is important for gastrin expression induced by H. pylori. | (21) PubMed: 22287591 | |
| 22 | CagL (210134741) | integrin αvβ6 | human | αvβ6 is a specific, high affinity receptor for CagL. | (22) PubMed: 31197920 | |
| 23 | CagY (210134729) | integrin α5β1 receptor | human | CagY interacts with α5β1 integrin, which acts like a molecular rheostat that modulates the host immune response to facilitate persistent infection. | (23) PubMed: 29764950 |
|
(1) Higashi H et al. (2002). SHP-2 tyrosine phosphatase as an intracellular target of Helicobacter pylori CagA protein. Science. 295(5555):683-6. [PudMed:11743164] |
|
(2) Mimuro H et al. (2002). Grb2 is a key mediator of helicobacter pylori CagA protein activities. Mol Cell. 10(4):745-55. [PudMed:12419219] |
|
(3) Saadat I et al. (2007). Helicobacter pylori CagA targets PAR1/MARK kinase to disrupt epithelial cell polarity. Nature. 447(7142):330-3. [PudMed:17507984] |
|
(4) Nešić D et al. (2014). Structure of the Helicobacter pylori CagA oncoprotein bound to the human tumor suppressor ASPP2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 111(4):1562-7. [PudMed:24474782] |
|
(5) Mishra JP et al. (2015). CagA of Helicobacter pylori interacts with and inhibits the serine-threonine kinase PRK2. Cell Microbiol. 17(11):1670-82. [PudMed:26041307] |
|
(6) Lee DG et al. (2014). Helicobacter pylori CagA promotes Snail-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition by reducing GSK-3 activity. Nat Commun. 5:4423. [PudMed:25055241] |
|
(7) Churin Y et al. (2003). Helicobacter pylori CagA protein targets the c-Met receptor and enhances the motogenic response. J Cell Biol. 161(2):249-55. [PudMed:12719469] |
|
(8) Murata-Kamiya N et al. (2007). Helicobacter pylori CagA interacts with E-cadherin and deregulates the beta-catenin signal that promotes intestinal transdifferentiation in gastric epithelial cells. Oncogene. 26(32):4617-26. [PudMed:17237808] |
|
(9) Murata-Kamiya N; Kikuchi K; Hayashi T; Higashi H; Hatakeyama M (2010). Helicobacter pylori exploits host membrane phosphatidylserine for delivery, localization, and pathophysiological action of the CagA oncoprotein. Cell Host Microbe. 7(5):399-411. [PudMed:20478541] |
|
(10) Poppe M; Feller SM; Romer G; Wessler S (2007). Phosphorylation of Helicobacter pylori CagA by c-Abl leads to cell motility. Oncogene. 26(24):3462-72. [PudMed:17160020] |
|
(11) Lim JW et al. (2009). alphaPix interacts with Helicobacter pylori CagA to induce IL-8 expression in gastric epithelial cells. Scand J Gastroenterol. 44(10):1166-72. [PudMed:19672789] |
|
(12) Amieva MR et al. (2003). Disruption of the epithelial apical-junctional complex by Helicobacter pylori CagA. Science. 300(5624):1430-4. [PudMed:12775840] |
|
(13) Kaplan-Türköz B et al. (2012). Structural insights into Helicobacter pylori oncoprotein CagA interaction with β1 integrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 109(36):14640-5. [PudMed:22908298] |
|
(14) Wang F et al. (2017). CagA promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of GES-1 cells by upregulating TRAF1/4-1BB. Mol Med Rep. 16(2):1262-1268. [PudMed:28627614] |
|
(15) Suzuki M et al. (2005). Interaction of CagA with Crk plays an important role in Helicobacter pylori-induced loss of gastric epithelial cell adhesion. J Exp Med. 202(9):1235-47. [PudMed:16275761] |
|
(16) Saju P et al. (2016). Host SHP1 phosphatase antagonizes Helicobacter pylori CagA and can be downregulated by Epstein-Barr virus. Nat Microbiol. 1:16026. [PudMed:27572445] |
|
(17) Lamb A et al. (2009). Helicobacter pylori CagA activates NF-kappaB by targeting TAK1 for TRAF6-mediated Lys 63 ubiquitination. EMBO Rep. 10(11):1242-9. [PudMed:19820695] |
|
(18) Mimuro H et al. (2007). Helicobacter pylori dampens gut epithelial self-renewal by inhibiting apoptosis, a bacterial strategy to enhance colonization of the stomach. Cell Host Microbe. 2(4):250-63. [PudMed:18005743] |
|
(19) Kwok T; Zabler D; Urman S; Rohde M; Hartig R; Wessler S; Misselwitz R; Berger J; Sewald N; Konig W; Backert S (2007). Helicobacter exploits integrin for type IV secretion and kinase activation. Nature. 449(7164):862-6. [PudMed:17943123] |
|
(20) Conradi J; Huber S; Gaus K; Mertink F; Royo Gracia S; Strijowski U; Backert S; Sewald N (2012). Cyclic RGD peptides interfere with binding of the Helicobacter pylori protein CagL to integrins alpha(V)beta (3) and alpha (5)beta (1). Amino Acids. 43(1):219-32. [PudMed:21915696] |
|
(21) Wiedemann T et al. (2012). Helicobacter pylori CagL dependent induction of gastrin expression via a novel αvβ5-integrin-integrin linked kinase signalling complex. Gut. 61(7):986-96. [PudMed:22287591] |
|
(22) Buß M et al. (2019). Specific high affinity interaction of Helicobacter pylori CagL with integrin αV β6 promotes type IV secretion of CagA into human cells. FEBS J. . [PudMed:31197920] |
|
(23) Skoog EC et al. (2018). CagY-Dependent Regulation of Type IV Secretion in Helicobacter pylori Is Associated with Alterations in Integrin Binding. MBio. 9(3). pii: e00717-18. [PudMed:29764950] |
|
(1) You Y; He L; Zhang M; Fu J; Gu Y; Zhang B; Tao X; Zhang J (2012). Comparative Genomics of Helicobacter pylori Strains of China Associated with Different Clinical Outcome. PLoS One. 7(6):e38528. [PudMed:22701658] |
| (2) Koch M; Mollenkopf HJ; Klemm U; Meyer TF (2012). Induction of microRNA-155 is TLR- and type IV secretion system-dependent in macrophages and inhibits DNA-damage induced apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 109(19):E1153-62. [PudMed:22509021] |
|
(3) Pham KT; Weiss E; Jimenez Soto LF; Breithaupt U; Haas R; Fischer W (2012). CagI is an essential component of the Helicobacter pylori Cag type IV secretion system and forms a complex with CagL. PLoS One. 7(4):e35341. [PudMed:22493745] |
|
(4) Jimenez-Soto LF; Rohrer S; Jain U; Ertl C; Sewald X; Haas R (2012). Effects of cholesterol on Helicobacter pylori growth and virulence properties in vitro. Helicobacter. 17(2):133-9. [PudMed:22404444] |
| (5) Backert S; Clyne M; Tegtmeyer N (2011). Molecular mechanisms of gastric epithelial cell adhesion and injection of CagA by Helicobacter pylori. Cell Commun Signal. 9:28. [PudMed:22044679] |
|
(6) Kumar Pachathundikandi S; Brandt S; Madassery J; Backert S (2011). Induction of TLR-2 and TLR-5 expression by Helicobacter pylori switches cagPAI-dependent signalling leading to the secretion of IL-8 and TNF-alpha. PLoS One. 6(5):e19614. [PudMed:21573018] |
|
(7) Schneider S; Carra G; Sahin U; Hoy B; Rieder G; Wessler S (2011). Complex cellular responses of Helicobacter pylori-colonized gastric adenocarcinoma cells. Infect Immun. 79(6):2362-71. [PudMed:21402757] |
| (8) Tegtmeyer N; Backert S (2011). Role of Abl and Src family kinases in actin-cytoskeletal rearrangements induced by the Helicobacter pylori CagA protein. Eur J Cell Biol. 90(11):880-90. [PudMed:21247656] |
|
(9) Fischer W; Windhager L; Rohrer S; Zeiller M; Karnholz A; Hoffmann R; Zimmer R; Haas R (2010). Strain-specific genes of Helicobacter pylori: genome evolution driven by a novel type IV secretion system and genomic island transfer. Nucleic Acids Res. 38(18):6089-101. [PudMed:20478826] |
|
(10) Saha A; Backert S; Hammond CE; Gooz M; Smolka AJ (2010). Helicobacter pylori CagL activates ADAM17 to induce repression of the gastric H, K-ATPase alpha subunit. Gastroenterology. 139(1):239-48. [PudMed:20303353] |
|
(11) Fehri LF; Rechner C; Janssen S; Mak TN; Holland C; Bartfeld S; Bruggemann H; Meyer TF (2009). Helicobacter pylori-induced modification of the histone H3 phosphorylation status in gastric epithelial cells reflects its impact on cell cycle regulation. Epigenetics. 4(8):577-86. [PudMed:20081355] |
|
(12) Jimenez-Soto LF; Kutter S; Sewald X; Ertl C; Weiss E; Kapp U; Rohde M; Pirch T; Jung K; Retta SF; Terradot L; Fischer W; Haas R (2009). Helicobacter pylori type IV secretion apparatus exploits beta1 integrin in a novel RGD-independent manner. PLoS Pathog. 5(12):e1000684. [PudMed:19997503] |
|
(13) Brandt S; Wessler S; Hartig R; Backert S (2009). Helicobacter pylori activates protein kinase C delta to control Raf in MAP kinase signalling: role in AGS epithelial cell scattering and elongation. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 66(10):874-92. [PudMed:19437514] |
|
(14) Svensson H; Hansson M; Kilhamn J; Backert S; Quiding-Jarbrink M (2009). Selective upregulation of endothelial E-selectin in response to Helicobacter pylori-induced gastritis. Infect Immun. 77(7):3109-16. [PudMed:19414551] |
|
(15) Hare S; Fischer W; Williams R; Terradot L; Bayliss R; Haas R; Waksman G (2007). Identification, structure and mode of action of a new regulator of the Helicobacter pylori HP0525 ATPase. EMBO J. 26(23):4926-34. [PudMed:17972918] |
|
(16) Kwok T; Zabler D; Urman S; Rohde M; Hartig R; Wessler S; Misselwitz R; Berger J; Sewald N; Konig W; Backert S (2007). Helicobacter exploits integrin for type IV secretion and kinase activation. Nature. 449(7164):862-6. [PudMed:17943123] |
|
(17) Pattis I; Weiss E; Laugks R; Haas R; Fischer W (2007). The Helicobacter pylori CagF protein is a type IV secretion chaperone-like molecule that binds close to the C-terminal secretion signal of the CagA effector protein. Microbiology. 153(Pt 9):2896-909. [PudMed:17768234] |
|
(18) Poppe M; Feller SM; Romer G; Wessler S (2007). Phosphorylation of Helicobacter pylori CagA by c-Abl leads to cell motility. Oncogene. 26(24):3462-72. [PudMed:17160020] |
|
(19) Garcia JT; Ferracci F; Jackson MW; Joseph SS; Pattis I; Plano LR; Fischer W; Plano GV (2006). Measurement of effector protein injection by type III and type IV secretion systems by using a 13-residue phosphorylatable glycogen synthase kinase tag. Infect Immun. 74(10):5645-57. [PudMed:16988240] |
|
(20) Backert S; Kwok T; Konig W (2005). Conjugative plasmid DNA transfer in Helicobacter pylori mediated by chromosomally encoded relaxase and TraG-like proteins. Microbiology. 151(Pt 11):3493-503. [PudMed:16272373] |
|
(21) Bauer B; Moese S; Bartfeld S; Meyer TF; Selbach M (2005). Analysis of cell type-specific responses mediated by the type IV secretion system of Helicobacter pylori. Infect Immun. 73(8):4643-52. [PudMed:16040977] |
|
(22) Wessler S; Rapp UR; Wiedenmann B; Meyer TF; Schoneberg T; Hocker M; Naumann M (2002). B-Raf/Rap1 signaling, but not c-Raf-1/Ras, induces the histidine decarboxylase promoter in Helicobacter pylori infection. FASEB J. 16(3):417-9. [PudMed:11790728] |
|
(23) Churin Y; Kardalinou E; Meyer TF; Naumann M (2001). Pathogenicity island-dependent activation of Rho GTPases Rac1 and Cdc42 in Helicobacter pylori infection. Mol Microbiol. 40(4):815-23. [PudMed:11401689] |
|
(24) Stein M; Rappuoli R; Covacci A; Blanke SR; Ye D; Odenbreit S; Gebert B; Puls J; Fischer W; Haas R (2001). Interaction of Helicobacter pylori with professional phagocytes: role of the cag pathogenicity island and translocation, phosphorylation and processing of CagA. Cell Microbiol. 3(1):21-31. [PudMed:11207617] |
|
(25) Ramarao N; Gray-Owen SD; Backert S; Meyer TF (2000). Helicobacter pylori inhibits phagocytosis by professional phagocytes involving type IV secretion components. Mol Microbiol. 37(6):1389-404. [PudMed:10998171] |
|
(26) Odenbreit S; Puls J; Sedlmaier B; Gerland E; Fischer W; Haas R (2000). Translocation of Helicobacter pylori CagA into gastric epithelial cells by type IV secretion. Science. 287(5457):1497-500. [PudMed:10688800] |