
| 2 | |
| Bartonella henselae str. Houston-1 | |
| chromosome [Browse all T4SS(s) in this replicon] | |
| NC_005956 | |
| 1512780..1525452 | |
| VirB | |
| effector translocation | |
| Type IVA; Type P | |
T4SS components |
| Component | VirB1 | VirB2 | VirB3 | VirB4 | VirB5 | VirB6 | VirB7 | VirB8 | VirB9 |
| Number | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Component | VirB10 | VirB11 | VirD4 | ||||||
| Number | 1 | 1 | 1 |
The information of T4SS components from NC_005956 | ||||||
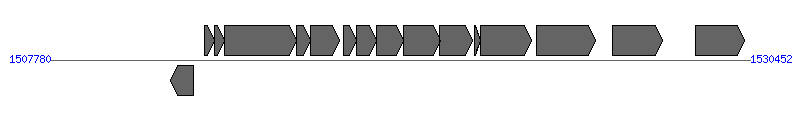 | ||||||
| # | Locus tag (Gene) | Coordinates [+/-], size (bp) | Protein GI | Product | Component | |
| 1 | BH13250 | 1511669..1512412 [-], 744 | 49476009 | hypothetical protein | ||
| 2 | BH13260 (virB2) | 1512780..1513103 [+], 324 | 49476010 | virB2 protein | VirB2 | |
| 3 | BH13270 (virB3) | 1513104..1513415 [+], 312 | 49476011 | virB3 protein | VirB3 | |
| 4 | BH13280 (virB4) | 1513421..1515775 [+], 2355 | 49476012 | virB4 protein | VirB4 | |
| 5 | BH13290 | 1515772..1516218 [+], 447 | 49476013 | hypothetical protein | VirB5 | |
| 6 | BH13300 (virB6) | 1516205..1517170 [+], 966 | 49476014 | virB protein | VirB6 | |
| 7 | BH13310 | 1517298..1517708 [+], 411 | 49476015 | hypothetical protein | VirB7 | |
| 8 | BH13320 (virB8) | 1517698..1518366 [+], 669 | 49476016 | virB8 protein | VirB8 | |
| 9 | BH13330 (virB9) | 1518366..1519229 [+], 864 | 49476017 | virB9 protein | VirB9 | |
| 10 | BH13340 (virB10) | 1519222..1520412 [+], 1191 | 49476018 | virB10 protein | VirB10 | |
| 11 | BH13350 (virB11) | 1520381..1521451 [+], 1071 | 49476019 | virB11 protein | VirB11 | |
| 12 | BH13360 | 1521519..1521725 [+], 207 | 49476020 | hypothetical protein | ||
| 13 | BH13370 | 1521736..1523370 [+], 1635 | 49476021 | cell filamentation protein | ||
| 14 | BH13380 (traG) | 1523533..1525452 [+], 1920 | 49476022 | conjugal transfer protein TraG | VirD4 | |
| 15 | BH13390 | 1525994..1527622 [+], 1629 | 49476023 | hypothetical protein | ||
| 16 | BH13400 | 1528692..1530290 [+], 1599 | 49476024 | cell filamentation protein | ||
Download FASTA format files |
| Proteins Genes |
| Crucial for establishment of infection in the primary niche- the endothelial cells, required for colonization of endothelial cells, by mediating the intracellular delivery of effector proteins (BepA-BepG). Translocation of the Beps provokes distinct cellular phenotypes: (i) a massive cytoskeleton rearrangement, resulting in the engulfment of bacterial aggregates (a phenotype called 'invasome' formation), (ii) NF-kappaB-dependent proinflammatory activation, characterized by chemokine secretion and expression of cell adhesion proteins, and (iii) enhanced cell survival as a result of anti-apoptosis (iv) capillary-like sprout formation of endothelial cell aggregates |
Effectors |
| BepA, BepB, BepC, BepD, BepE, BepF, BepG |
The information of protein effectors | ||||||
| # | Locus tag (Gene) | Coordinates [+/-], size (bp) | Protein GI | Product | * | |
| 1 | BH13370 | 1521736..1523370 [+], 1635 | 49476021 | cell filamentation protein | ||
| 2 | BH13390 | 1525994..1527622 [+], 1629 | 49476023 | hypothetical protein | ||
| 3 | BH13400 | 1528692..1530290 [+], 1599 | 49476024 | cell filamentation protein | ||
| 4 | BH13410 | 1530764..1532368 [+], 1605 | 49476025 | hypothetical protein | ||
| 5 | BH13420 | 1532694..1534088 [+], 1395 | 49476026 | hypothetical protein | ||
| 6 | BH13430 | 1534424..1536928 [+], 2505 | 49476027 | hypothetical protein | ||
| 7 | BH13440 | 1537113..1540244 [+], 3132 | 49476028 | hypothetical protein | ||
Download FASTA format files |
| Proteins Genes |
| # | Name | Image | Resource | Detail | Reference |
| 1 | BepA | 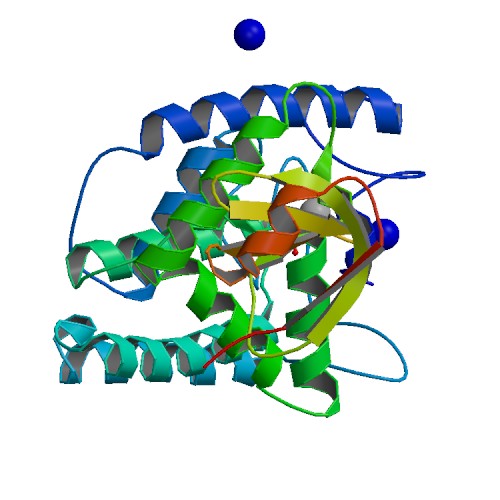 | PDB (2JK8) | Type IV secretion system effector protein BepA complexed with a pyrophosphate moiety. | (1) PubMed: 21213248 |
| 2 | BepE | 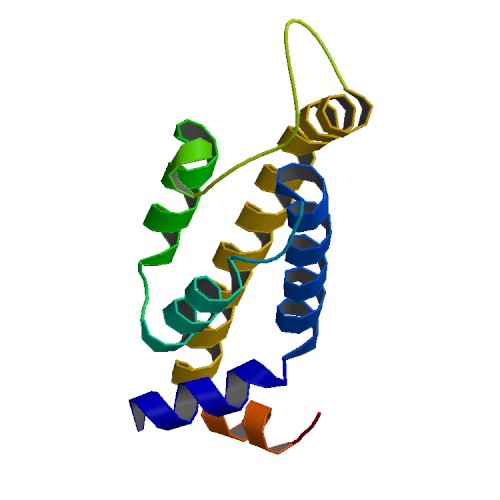 | PDB (4YK3) | Crystal Structure of the BID Domain of BepE from Bartonella henselae. | (2) PubMed: 27889208 |
|
(1) Palanivelu DV; Goepfert A; Meury M; Guye P; Dehio C; Schirmer T (2011). Fic domain-catalyzed adenylylation: insight provided by the structural analysis of the type IV secretion system effector BepA. Protein Sci. 20(3):492-9. [PudMed:21213248] |
|
(2) Stanger FV et al. (2017). The BID Domain of Type IV Secretion Substrates Forms a Conserved Four-Helix Bundle Topped with a Hook. Structure. 25(1):203-211. [PudMed:27889208] |
| # | Name(Protein GI) | Host site/Substrate | Source | Function | Reference | |
| 1 | BepA (49476021) | Adenylyl cyclase | human | BepA is located on the plasma membrane and triggers the production of second messenger cyclic adenosine monophosphate to repress endothelial cell (EC) apoptosis. | (1) PubMed: 17121462 | |
| 2 | BepC (49476024) | unknown | unknown | The combined action of BepC and BepF triggers the formation of invasome and repress endocytic uptake of inert microspheres. | (2) PubMed: 20964799 | |
| 3 | BepE (49476026) | unknown | unknown | BepE protects infected migratory cells from BepC's injurious and restores normal cell migration through the RhoA signaling pathway. | (3) PubMed: 24945914 | |
| 4 | BepF (49476027) | unknown | unknown | The combined action of BepC and BepF triggers the formation of invasome and repress endocytic uptake of inert microspheres. Besides, BepF play a role in activation of Rac1 and Cdc42 during the invasome formation process. | (4) PubMed: 22043280 | |
| 5 | BepG (49476028) | unknown | unknown | BepG repress bacterial endocytosis to triggers invasome-mediated internalization. | (5) PubMed: 19302579 |
|
(1) Schmid MC; Scheidegger F; Dehio M; Balmelle-Devaux N; Schulein R; Guye P; Chennakesava CS; Biedermann B; Dehio C (2006). A translocated bacterial protein protects vascular endothelial cells from apoptosis. PLoS Pathog. 2(11):e115. [PudMed:17121462] |
|
(2) Truttmann MC; Rhomberg TA; Dehio C (2011). Combined action of the type IV secretion effector proteins BepC and BepF promotes invasome formation of Bartonella henselae on endothelial and epithelial cells. Cell Microbiol. 13(2):284-99. [PudMed:20964799] |
|
(3) Okujava R et al. (2014). A translocated effector required for Bartonella dissemination from derma to blood safeguards migratory host cells from damage by co-translocated effectors. PLoS Pathog. 10(6):e1004187. [PudMed:24945914] |
|
(4) Truttmann MC; Guye P; Dehio C (2011). BID-F1 and BID-F2 domains of Bartonella henselae effector protein BepF trigger together with BepC the formation of invasome structures. PLoS One. 6(10):e25106. [PudMed:22043280] |
|
(5) Rhomberg TA; Truttmann MC; Guye P; Ellner Y; Dehio C (2009). A translocated protein of Bartonella henselae interferes with endocytic uptake of individual bacteria and triggers uptake of large bacterial aggregates via the invasome. Cell Microbiol. 11(6):927-45. [PudMed:19302579] |
|
(1) Guy L; Nystedt B; Sun Y; Naslund K; Berglund EC; Andersson SG (2012). A genome-wide study of recombination rate variation in Bartonella henselae. BMC Evol Biol. 12(1):65. [PudMed:22577862] |
|
(2) Truttmann MC; Misselwitz B; Huser S; Hardt WD; Critchley DR; Dehio C (2011). Bartonella henselae engages inside-out and outside-in signaling by integrin beta1 and talin1 during invasome-mediated bacterial uptake. J Cell Sci. 124(Pt 21):3591-602. [PudMed:22045736] |
|
(3) Fernandez-Gonzalez E; de Paz HD; Alperi A; Agundez L; Faustmann M; Sangari FJ; Dehio C; Llosa M (2011). Transfer of R388 derivatives by a pathogenesis-associated type IV secretion system into both bacteria and human cells. J Bacteriol. 193(22):6257-65. [PudMed:21908662] |
|
(4) Schroder G; Schuelein R; Quebatte M; Dehio C (2011). Conjugative DNA transfer into human cells by the VirB/VirD4 type IV secretion system of the bacterial pathogen Bartonella henselae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 108(35):14643-8. [PudMed:21844337] |
|
(5) Scheidegger F; Quebatte M; Mistl C; Dehio C (2011). The Bartonella henselae VirB/Bep system interferes with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signalling in human vascular endothelial cells. Cell Microbiol. 13(3):419-31. [PudMed:21044238] |
|
(6) Truttmann MC; Rhomberg TA; Dehio C (2011). Combined action of the type IV secretion effector proteins BepC and BepF promotes invasome formation of Bartonella henselae on endothelial and epithelial cells. Cell Microbiol. 13(2):284-99. [PudMed:20964799] |
|
(7) Quebatte M; Dehio M; Tropel D; Basler A; Toller I; Raddatz G; Engel P; Huser S; Schein H; Lindroos HL; Andersson SG; Dehio C (2010). The BatR/BatS two-component regulatory system controls the adaptive response of Bartonella henselae during human endothelial cell infection. J Bacteriol. 192(13):3352-67. [PudMed:20418395] |
|
(8) Scheidegger F; Ellner Y; Guye P; Rhomberg TA; Weber H; Augustin HG; Dehio C (2009). Distinct activities of Bartonella henselae type IV secretion effector proteins modulate capillary-like sprout formation. Cell Microbiol. 11(7):1088-101. [PudMed:19416269] |
|
(9) Schulein R; Guye P; Rhomberg TA; Schmid MC; Schroder G; Vergunst AC; Carena I; Dehio C (2005). A bipartite signal mediates the transfer of type IV secretion substrates of Bartonella henselae into human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 102(3):856-61. [PudMed:15642951] |
|
(10) Schmid MC; Schulein R; Dehio M; Denecker G; Carena I; Dehio C (2004). The VirB type IV secretion system of Bartonella henselae mediates invasion, proinflammatory activation and antiapoptotic protection of endothelial cells. Mol Microbiol. 52(1):81-92. [PudMed:15049812] |
|
(11) Schmiederer M; Arcenas R; Widen R; Valkov N; Anderson B (2001). Intracellular induction of the Bartonella henselae virB operon by human endothelial cells. Infect Immun. 69(10):6495-502. [PudMed:11553594] |