
| 812 | |
| Escherichia coli plasmid R388 (NC_028464) | |
| plasmid R388 [Browse all T4SS(s) in this replicon] | |
| NC_028464 | |
| 1020..15650 | |
| Trw | |
| Conjugation | |
| Type IVA; Type P | |
T4SS components |
| Component | TrwB | TrwD | TrwE | TrwF | TrwG | TrwH | TrwI | TrwJ | TrwK |
| Number | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Component | TrwL | TrwM | TrwN | ||||||
| Number | 1 | 1 | 1 |
The information of T4SS components from NC_028464 | ||||||
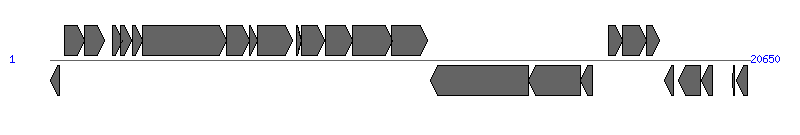 | ||||||
| # | Locus tag (Gene) | Coordinates [+/-], size (bp) | Protein GI | Product | Component | |
| 1 | - (korB) | 1..288 [-], 288 | 971848294 | putative transcriptional repressor | ||
| 2 | - | 425..1018 [+], 594 | 971848295 | hypothetical protein | ||
| 3 | - (trwN) | 1020..1616 [+], 597 | 971848296 | TrwN protein | TrwN | |
| 4 | - (korA) | 1841..2137 [+], 297 | 971848297 | putative transcriptional repressor | ||
| 5 | - (trwL) | 2070..2408 [+], 339 | 971848298 | TrwL protein | TrwL | |
| 6 | - (trwM) | 2421..2735 [+], 315 | 971848299 | TrwM protein | TrwM | |
| 7 | - (trwK) | 2738..5209 [+], 2472 | 971848300 | TrwK protein | TrwK | |
| 8 | - (trwJ) | 5206..5886 [+], 681 | 971848301 | TrwJ protein | TrwJ | |
| 9 | - (eex) | 5883..6113 [+], 231 | 971848302 | entry exclusion protein | ||
| 10 | - (trwI) | 6127..7155 [+], 1029 | 971848303 | TrwI protein | TrwI | |
| 11 | - (trwH) | 7269..7412 [+], 144 | 971848304 | TrwH protein | TrwH | |
| 12 | - (trwG) | 7409..8104 [+], 696 | 971848305 | TrwG protein | TrwG | |
| 13 | - (trwF) | 8115..8915 [+], 801 | 971848306 | TrwF protein | TrwF | |
| 14 | - (trwE) | 8915..10102 [+], 1188 | 971848307 | TrwE protein | TrwE | |
| 15 | - (trwD) | 10068..11144 [+], 1077 | 971848308 | TrwD protein | TrwD | |
| 16 | - (trwC) | 11227..14127 [-], 2901 | 971848309 | TrwC protein | ||
| 17 | - (trwB) | 14127..15650 [-], 1524 | 971848310 | TrwB protein | TrwB | |
| 18 | - (trwA) | 15652..16017 [-], 366 | 971848311 | TrwA protein | ||
| 19 | - | 16471..16896 [+], 426 | 971848312 | hypothetical protein | ||
| 20 | - | 16893..17588 [+], 696 | 971848313 | hypothetical protein | ||
| 21 | - | 17602..17988 [+], 387 | 971848314 | hypothetical protein | ||
| 22 | - | 18142..18393 [-], 252 | 971848315 | hypothetical prootein | ||
| 23 | - | 18541..19194 [-], 654 | 971848316 | hypothetical protein | ||
| 24 | - | 19210..19554 [-], 345 | 971848317 | hypothetical protein | ||
| 25 | - | 20139..20207 [-], 69 | 971848318 | hypothetical protein | ||
| 26 | - | 20247..20570 [-], 324 | 971848319 | hypothetical protein | ||
Download FASTA format files |
| Proteins Genes |
| # | Name | Image | Resource | Detail | Reference |
| 1 | T4SS3−10 complex | 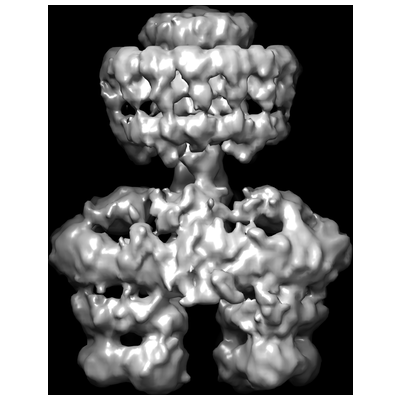 | EMDB(2567) | T4SS3−10 complex from the E. coli R388 plasmid | (1) PubMed: 24670658 |
| 2 | The outer membrane complex | PDB (3JQO ) | Crystal structure of the outer membrane complex | (2) PubMed: 19946264 | |
| 3 | TrwB | 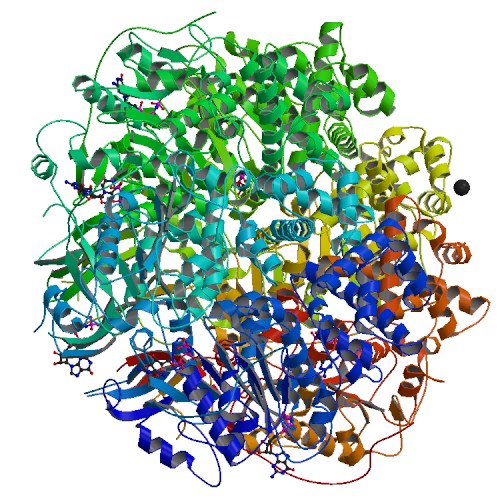 | PDB (1GL6) | Plasmid coupling protein | (3) PubMed: 11214325 |
| 4 | TrwBdeltaN70 | 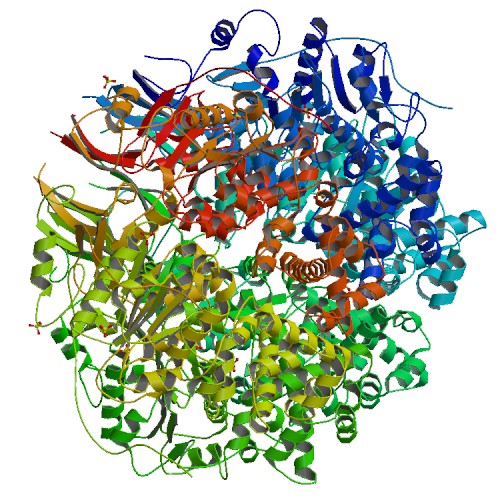 | PDB (1E9R) | Bacterial conjugative coupling protein TrwBdeltaN70. Trigonal form in complex with sulphate. | (4) PubMed: 11214325 |
| 5 | TrwB in complex with the non-hydrolisable ATP-analogue ADPNP | 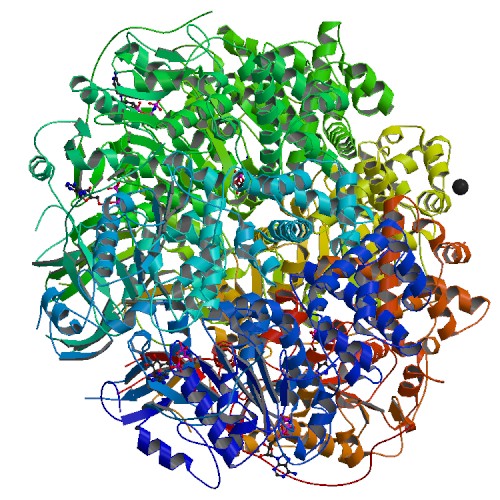 | PDB (1GL7) | Plasmid coupling protein TrwB in complex with the non-hydrolisable ATP-analogue ADPNP | (5) PubMed: 11214325 |
| 6 | TrwB with ADP and Mg2+ | 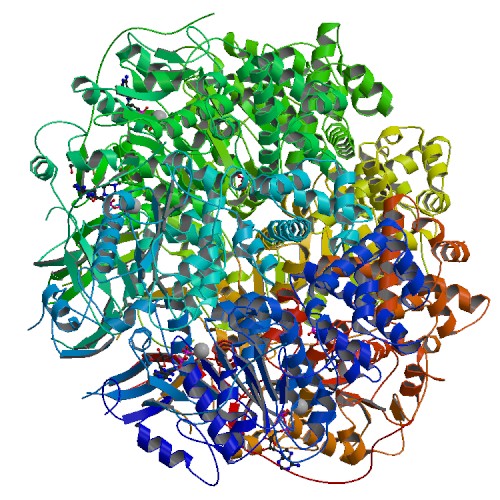 | PDB (1GKI) | Plasmid coupling protein TrwB in complex with ADP and Mg2+. | (6) PubMed: 11214325 |
| 7 | TrwBΔN70 | PDB (1E9S ) | Bacterial conjugative coupling protein TrwBdeltaN70. Unbound monoclinic form. | (7) PubMed: 11214325 | |
| 8 | TrwC bound with oriT ssDNA | 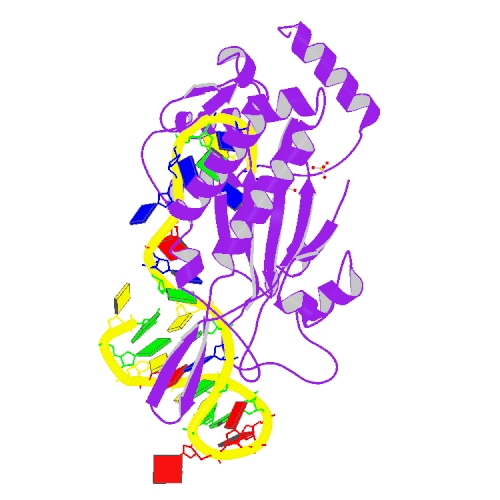 | PDB (1OMH) | Crystal structure of the transesterase domain of R388 relaxase TrwC bound with 25mer oriT single-stranded (ss)DNA | (8) PubMed: 14625590 |
| 9 | VirD4 bound to a Type IV secretion system | 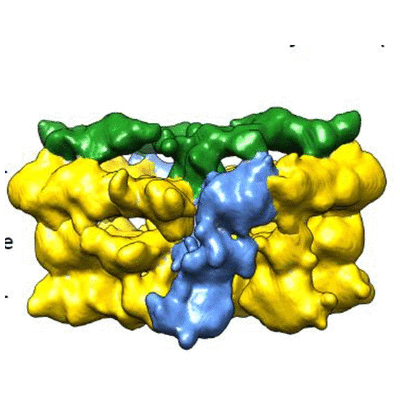 | EMDB(3585) | Structure of the VirD4 bound to a Type IV secretion system. | (9) PubMed: 28923826 |
|
(1) Low HH et al. (2014). Structure of a type IV secretion system. Nature. 508(7497):550-553. [PudMed:24670658] |
|
(2) Chandran V; Fronzes R; Duquerroy S; Cronin N; Navaza J; Waksman G (2009). Structure of the outer membrane complex of a type IV secretion system. Nature. 462(7276):1011-5. [PudMed:19946264] |
|
(3) Gomis-Rüth FX et al. (2001). The bacterial conjugation protein TrwB resembles ring helicases and F1-ATPase. Nature. 409(6820):637-41.. [PudMed:11214325] |
|
(4) Gomis-Rüth FX et al. (2001). The bacterial conjugation protein TrwB resembles ring helicases and F1-ATPase. Nature. 409(6820):637-41.. [PudMed:11214325] |
|
(5) Gomis-Rüth FX et al. (2001). The bacterial conjugation protein TrwB resembles ring helicases and F1-ATPase. Nature. 409(6820):637-41.. [PudMed:11214325] |
|
(6) Gomis-Rüth FX et al. (2001). The bacterial conjugation protein TrwB resembles ring helicases and F1-ATPase. Nature. 409(6820):637-41.. [PudMed:11214325] |
|
(7) Gomis-Rüth FX et al. (2001). The bacterial conjugation protein TrwB resembles ring helicases and F1-ATPase. Nature. 409(6820):637-41.. [PudMed:11214325] |
|
(8) Guasch A et al. (2003). Recognition and processing of the origin of transfer DNA by conjugative relaxase TrwC. Nat Struct Biol. 10(12):1002-10. [PudMed:14625590] |
|
(9) Redzej A et al. (2017). Structure of a VirD4 coupling protein bound to a VirB type IV secretion machinery. EMBO J. 36(20):3080-3095. [PudMed:28923826] |
| # | Accessory protein(GI) | motif(s) | Substrate(s) | Function | Reference |
| 1 | TrwA (971848311) | ND (interacts with TrwB T4CP) | TrwC | TrwA is RHH DNA binding tetramer protein which stimulates T4CP ATP hydrolysis. TrwA protein enhances the effects of DNA on TrwB ATPase activity. | (1) PubMed: 17599913 |
|
(1) Tato I et al. (2007). The ATPase activity of the DNA transporter TrwB is modulated by protein TrwA: implications for a common assembly mechanism of DNA translocating motors. J Biol Chem. 282(35):25569-76. [PudMed:17599913] |
| (1) Grohmann E et al. (2018). Type IV secretion in Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria.. Mol Microbiol. 107(4):455-471.. [PudMed:29235173] |
|
(2) Christie PJ (2016). The Mosaic Type IV Secretion Systems. EcoSal Plus. 7(1). [PudMed:27735785] |
| (3) Chandran Darbari V et al. (2015). Structural Biology of Bacterial Type IV Secretion Systems. Annu Rev Biochem. 84:603-29. [PudMed:26034891] |
| (4) Ilangovan A et al. (2015). Structural biology of the Gram-negative bacterial conjugation systems. Trends Microbiol. 23(5):301-10. [PudMed:25825348] |