The graph information of MGIVvuTai1 components from BA000037 |
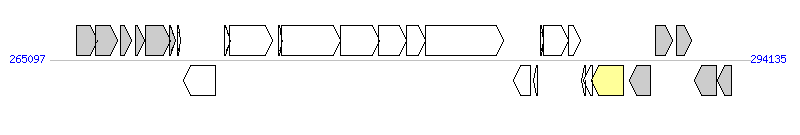 |
| Complete gene list of MGIVvuTai1 from BA000037 |
| # | Gene | Coordinates [+/-], size (bp) | Product | *Reannotation  |
| 1 | VV0254 | 266185..267054 [+], 870 | ABC-type oligopeptide transport system, ATPase component | |
| 2 | VV0255 | 266984..267904 [+], 921 | ABC-type oligopeptide transport system, ATPase component | |
| 3 | VV0256 | 268030..268473 [+], 444 | conserved hypothetical protein | |
| 4 | VV0257 | 268628..269011 [+], 384 | hypothetical protein | |
| 5 | VV0258 | 269057..270097 [+], 1041 | putative membrane protein | |
| 6 | VV0259 | 270073..270300 [+], 228 | hypothetical protein | |
| 7 | VV0260 | 270370..270498 [+], 129 | hypothetical protein | |
| 8 | VV0261 | 270633..271952 [-], 1320 | conserved hypothetical protein | |
| 9 | VV0262 | 272326..272583 [+], 258 | conserved hypothetical protein | |
| 10 | VV0263 | 272561..274309 [+], 1749 | conserved hypothetical protein | |
| 11 | VV0264 | 274559..274756 [+], 198 | VrlI homologue | |
| 12 | VV0265 | 274695..277148 [+], 2454 | type I site-specific restriction-modification system, R (restriction) subunit | |
| 13 | VV0266 | 277154..278746 [+], 1593 | type I restriction-modification system methyltransferase subunit | |
| 14 | VV0267 | 278743..279885 [+], 1143 | type I restriction-modification enzyme, specificity subunit | |
| 15 | VV0268 | 279885..280682 [+], 798 | hypothetical protein | |
| 16 | VV0269 | 280679..283921 [+], 3243 | hypothetical protein | |
| 17 | VV0270 | 284319..285020 [-], 702 | hypothetical protein | |
| 18 | VV0271 | 285144..285329 [-], 186 | hypothetical protein | |
| 19 | VV0272 | 285448..285567 [+], 120 | hypothetical protein | |
| 20 | VV0273 | 285564..286616 [+], 1053 | hypothetical protein | |
| 21 | VV0274 | 286617..287096 [+], 480 | hypothetical protein | |
| 22 | VV0275 | 287147..287317 [-], 171 | hypothetical protein | |
| 23 | VV0276 | 287229..287606 [-], 378 | hypothetical protein | |
| 24 | VV0277 | 287569..288873 [-], 1305 | site-specific recombinase, phage integrase family | Integrase |
| 25 | VV0278 | 289135..290022 [-], 888 | uncharacterized stress-induced protein | |
| 26 | VV0279 | 290211..290927 [+], 717 | RNase PH | |
| 27 | VV0280 | 291084..291725 [+], 642 | orotate phosphoribosyltransferase | |
| 28 | VV0281 | 291825..292763 [-], 939 | lipid A biosynthesis lauroyl acyltransferase | |
| 29 | VV0282 | 292767..293357 [-], 591 | transcriptional regulator | |

