The graph information of MGIVflInd1 components from KC117176 |
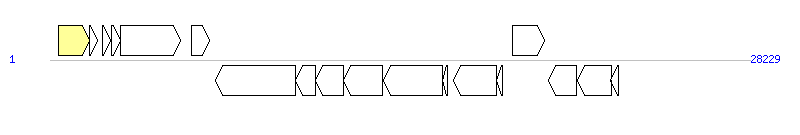 |
| Complete gene list of MGIVflInd1 from KC117176 |
| # | Gene | Coordinates [+/-], size (bp) | Product | *Reannotation  |
| 1 | int | 340..1590 [+], 1251 | integrase family tyrosine site-specific recombinase | Integrase |
| 2 | MGIVFLIND1_002 | 1592..1930 [+], 339 | conserved hypothetical protein | |
| 3 | MGIVFLIND1_003 | 2126..2428 [+], 303 | conserved hypothetical protein | |
| 4 | MGIVFLIND1_004 | 2460..2831 [+], 372 | helix-turn-helix domain-containing protein | |
| 5 | MGIVFLIND1_005 | 2857..5265 [+], 2409 | DEAD/DEAH box helicase | |
| 6 | MGIVFLIND1_006 | 5723..6421 [+], 699 | conserved hypothetical protein | |
| 7 | MGIVFLIND1_007 | 6672..9914 [-], 3243 | DEAD/DEAH box helicase | |
| 8 | MGIVFLIND1_008 | 9911..10708 [-], 798 | conserved hypothetical protein | |
| 9 | hsdS | 10708..11850 [-], 1143 | type I restriction-modification enzyme, specificity subunit | |
| 10 | hsdM | 11847..13424 [-], 1578 | type I restriction-modification enzyme, methyltransferase subunit | |
| 11 | hsdR | 13445..15835 [-], 2391 | type I restriction-modification enzyme, restriction subunit | |
| 12 | MGIVFLIND1_012 | 15837..16034 [-], 198 | VrlI-like protein | |
| 13 | MGIVFLIND1_013 | 16284..18026 [-], 1743 | hypothetical protein | |
| 14 | rdfM | 18013..18255 [-], 243 | recombination directionality factor | |
| 15 | MGIVFLIND1_015 | 18648..19961 [+], 1314 | putative AAA+ ATPase | |
| 16 | MGIVFLIND1_016 | 20105..21223 [-], 1119 | hypothetical protein | |
| 17 | MGIVFLIND1_017 | 21278..22627 [-], 1350 | HipA domain-containing protein | |
| 18 | MGIVFLIND1_018 | 22617..22940 [-], 324 | helix-turn-helix domain transcriptional regulator | |