
| How to use TAfinder ?Step-by-Step Tutorial |
|
|
| |
| Input data - Compare [TOP] | |
| "Compare" provides you a solution to view the distribution of all the predicted TA loci among various genomes, which you may be interested in. By this, it is possible to figure out the conserved TA loci and the specific. STEP 1: (1) You will be asked to input your TA locus(loci). (2) You can either paste your sequences or upload your sequences in FASTA format. 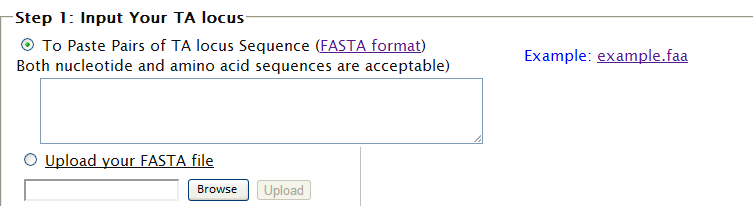 (3) Toxin and Antitoxin are both necessary for defining a TA locus, so component and relationship must be reflected in the specified format in the sequence. The format is as follows: ">TA_1_T_123456789" for Toxin in pair 1 while ">TA_1_AT_987654321" for cognate Antitoxin. If you submit your TA locus sequences without marking these information, your sequences will be identified as TA locus by sequence order with Toxin in front of Antitoxin. Example: 4 sequences with ">example1",">example2",">example3",">example4" by order, will be identified as ">TA_1_T_example1",">TA_1_AT_example2",">TA_2_T_example3",">TA_2_AT_example4".  STEP 2: (1) Choose your subject genome(s) by accession number or select from "genome list". (2) Accession numbers should be separated by "return". (3) After selecting subject genome(s), click finish to submit accession number(s). You can click "[TOP]" and back to "finish" easily.  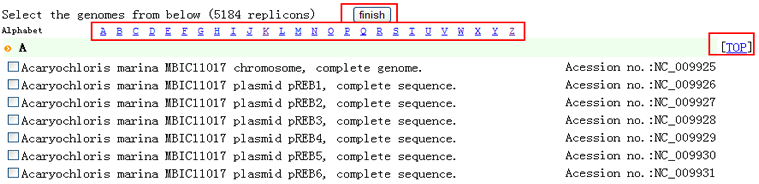 STEP 3: Set parameters and click "Run". 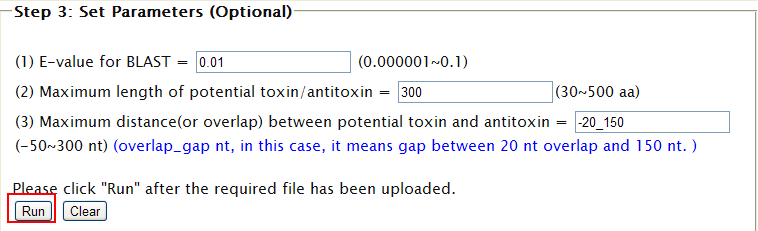 |
|
| Run TAfinder - Compare [TOP] | |
When TAfinder - Compare is running, the following page will be shown to users. 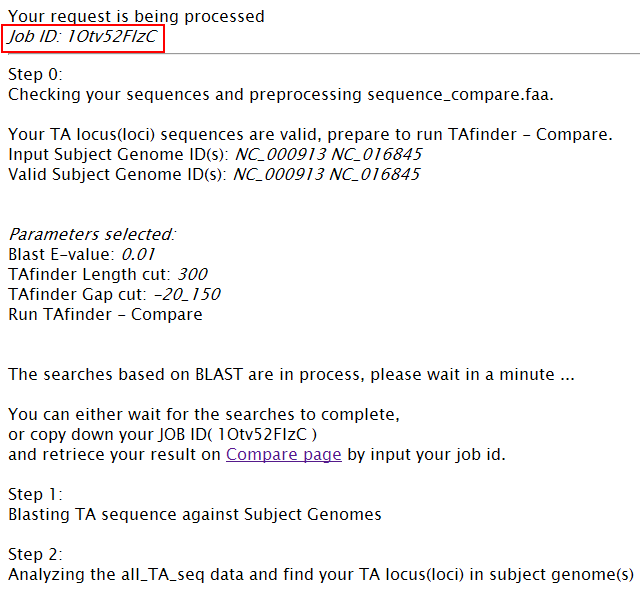 Note: (1) You can define the rule to get conserved or specific results. 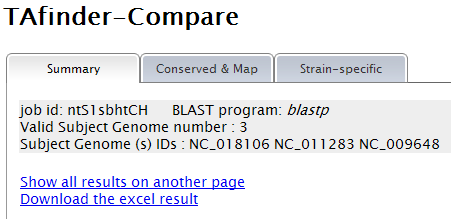 More details about H-value in rule1 please see More about parameter: what is H-value?  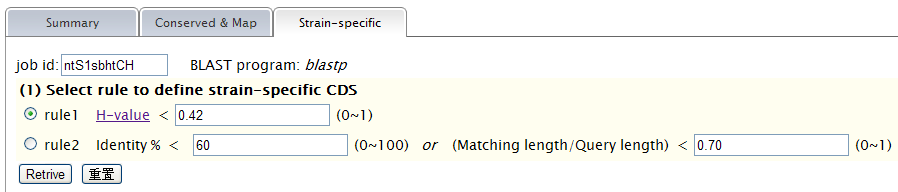 (2) All results are listed on this page, and you can download them in excel format as well. The name of each locus is a hyperlink, which allows all hits matching this TA locus from subject genomes to be shown, after you click it. 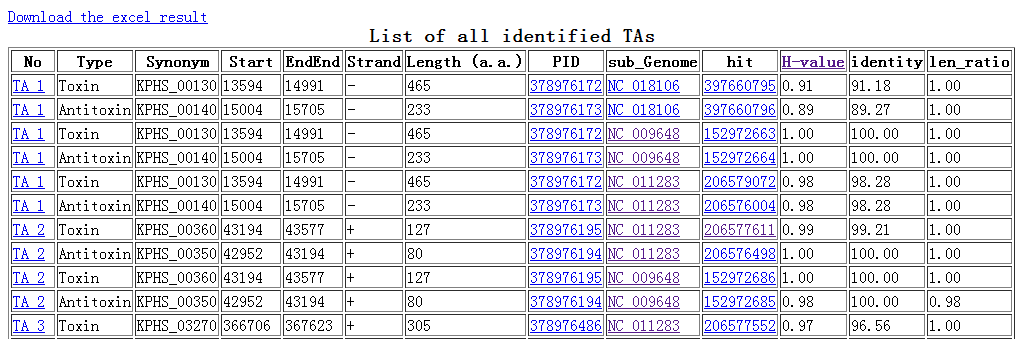 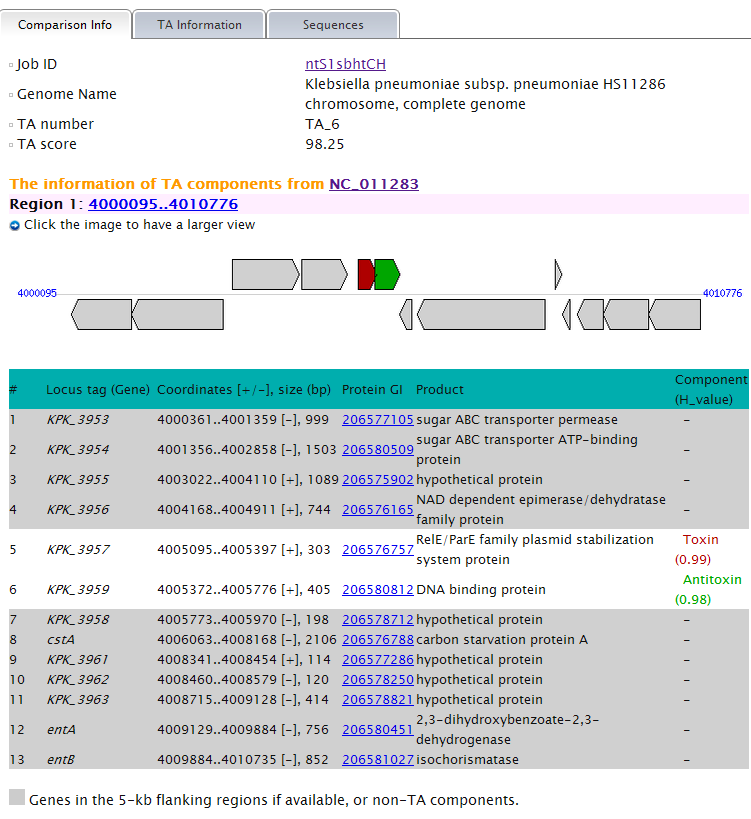 |
|
| Input data - Predict [TOP] | |
| Sequence data in FASTA, PTT, GenBank format could be accepted by TAfinder. Two separate files may be requested, in the case of some input method. Choose the proper input and click "run". When uploading your own sequences, please "Browse" to find the path and then "Upload", for each file.
Details on each input pattern will be introduced as followed.   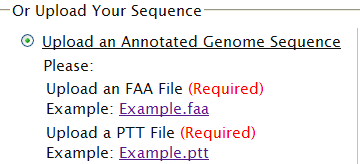 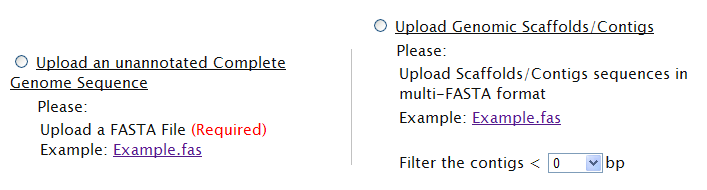 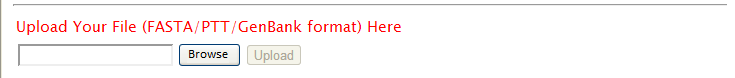 |
|
| A pair of gene/protein sequences [TOP] | |
| If you already have got a pair of nucleotide or amino acid sequences, to find a TA locus, please input your sequences in the box below. Each sequence should be in FASTA format. Briefly, they should begin with a single-line description, which is distinguished from the sequence data by a greater-than (">") symbol in the first column. Also, please provide the coordinates of each sequence in the corresponding genome. Note: (1) Please input TWO separate sequences in the box below. (2) The defult values of the Coordinate in genome fit the example. You can copy the example for test. 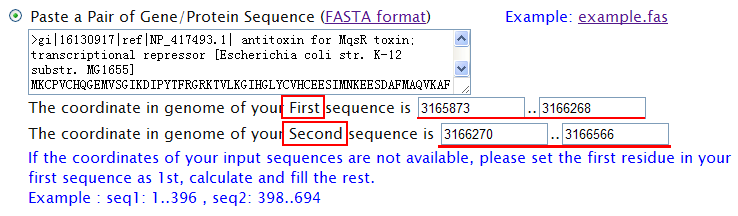
|
|
| Select a completely sequenced bacterial genome [TOP] | |
| For a completely sequenced genome to be analyzed, you can easily choose its name on genome list page. Note: (1) All genomes listed below are from NCBI database (ftp), newly released data may not be included.  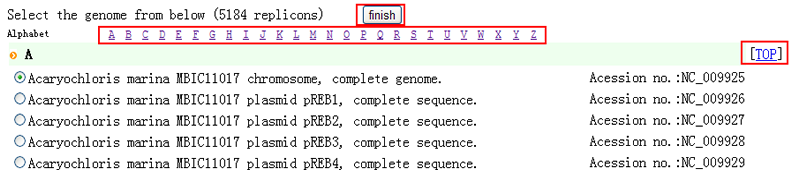 
|
|
| Input an accession number [TOP] | |
| If you have the NCBI accession number of a completely sequenced bacterial genome ready to use, no doubt that this is accepted by TAfinder. Please choose that option below and enter a accession number in the box. Note: All genomes listed below are from NCBI database (ftp), newly released data may not be included. 
|
|
| Upload your own sequences [TOP] | |
| Sequence files from users’ own collection could also be accepted by TAfinder. As TAfinder may use different algorithms depending on the formats of data input, please submit your sequences following the instruction in different modules. |
|
| Your sequences are well annotated [TOP] | |
| If your sequences are well annotated, BOTH FAA and PTT file will be required. A FAA file containsamino acid sequences in FASTA format. Example.faa A PTT file contains information of proteins including location and length etc. Example.ptt  More About Format: (1) A multiple sequence faa file looks like this: 
(2) A ptt file looks like this: 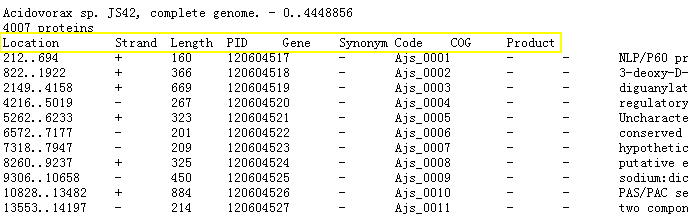
(3) A GenBank file can be used to generate a PTT file, and the full GenBank file, which includes amino acid sequence, could be used to generate both PTT and FAA file. Thus, either type of GenBank file could be accepted, but please make sure that both FAA and PTT files could be generated or uploaded directly. For example, this Genbank file can generate ptt file only: 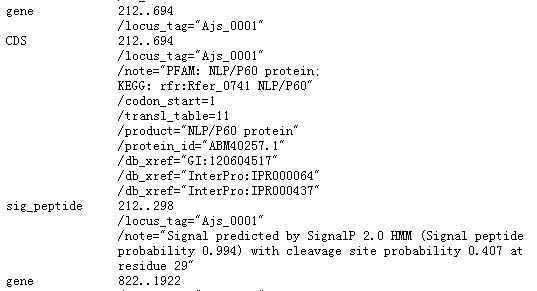
This Genbank file can generate both faa file and ptt file: 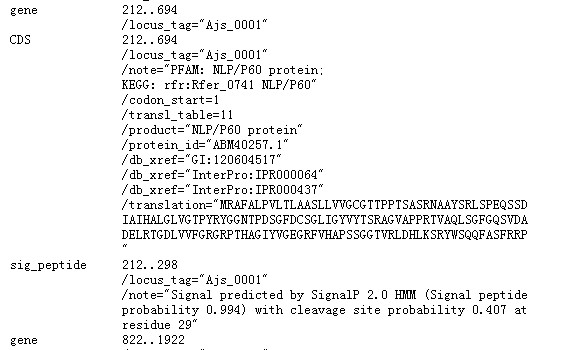
|
|
| Your sequences are completely sequenced without annotation [TOP] | |
There is no worry about the complete genomic sequence file without annotation, it is acceptable in TAfinder as well. This type of file will be annotated briefly by TAfinder, before processing. 
Note: (1) Example sequence: 
|
|
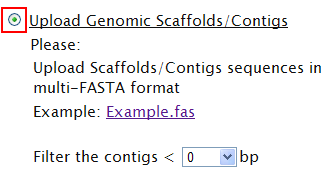
| Your have only partial sequences (contigs or scaffolds) [TOP] | |
If you have only partial sequences, don’t worry! Sequence file of either contigs or scaffolds is acceptable! Please upload these files and define a lower threshold for filter. For example, if you set 500 bp as the threshold, any contigs shorter than 500 bp will be filtered out. If default, all contigs input will be taken into analysis.
|
|
| Run TAfinder - Predict [TOP] | |
Get your input ready? TAfinder will start to find TA loci immediately after you click the button “Run”.  Note: Depending on your input, the time consuming of TAfinder may vary. Generally, unannotated input requires more analysis time. When TAfinder is running, the following page will be shown to users.  |
|
| Retrieve results - Predict [TOP] | |
| You can get the analysis results with the Job ID or the link (shown in blue) provided on the running page.
Note: Please note that there is NO SPACE in your job ID provided by TAfinder. As the Job ID is generated randomly, and may be not so easy to remember, we recommend that you just copy it to your clipboard, and paste when you retrieve the result. Sorry for the inconvenience it may cause. 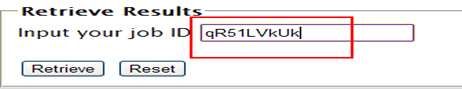 |
|
| Report of job [TOP] | |
|
Your analysis result is shown on the report page. Various information is given and organized under four tabs (TA list, Map, Download and Compare). The "Compare" tab is introduced at Compare--distribution analysis of TA loci among other species.
Note: (1) All TA loci predicted by TAfinder are shown under the "TA list" tab, you can find all the related information here as well. If you need further detail of each locus or family, please click on the link shown in blue. 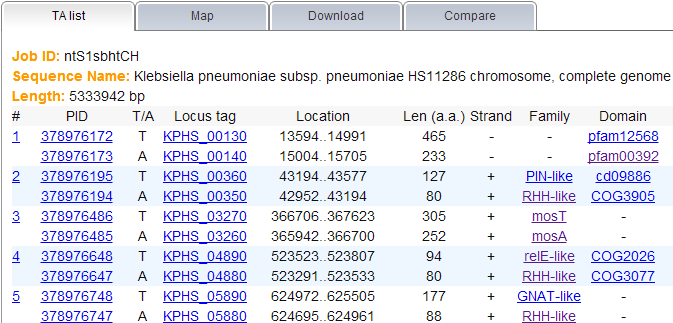 (2) The content under "Map" tab allows user to view the predicted TA loci in genome with a visual display. Please note that this map only could be shown in the case that you input a complete genome, either by selecting one in the given list or entering a valid accession number. 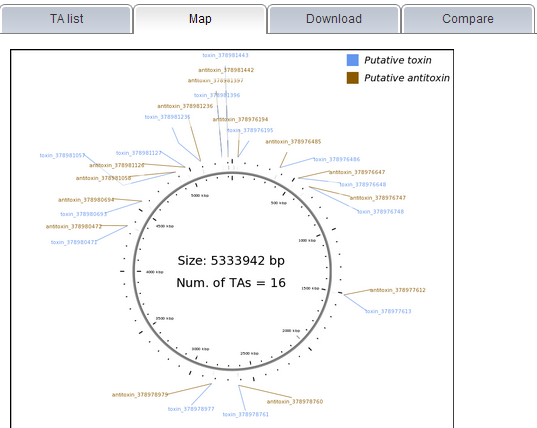 (3) Links are provided to download your results, under the "Download" tab in the report page. If you input a complete genomic sequence without annotation or partially sequenced genome, genes predicted by Prodigal or amino acid sequence translated by EMBOSS would be ready to download as well. 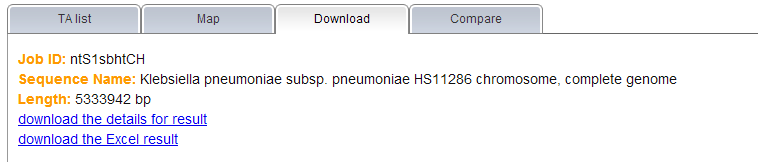 | |
| Detail about each TA locus [TOP] | |
|
More detail, say TA information, sequence and alignment tool are provided for each predicted TA locus, if you click the links of them. They are organized in three modules and shown under separate tabs. A primer design tool is integrated in the "Sequence" tab. More information of the "Alignment" tab is given in the part Context--GI ( Genomic Island) related elements analysis in TA context. of this instruction. Note: (1) TA information shows all the information that could be provided by TAfinder in detail, of each predicted locus. 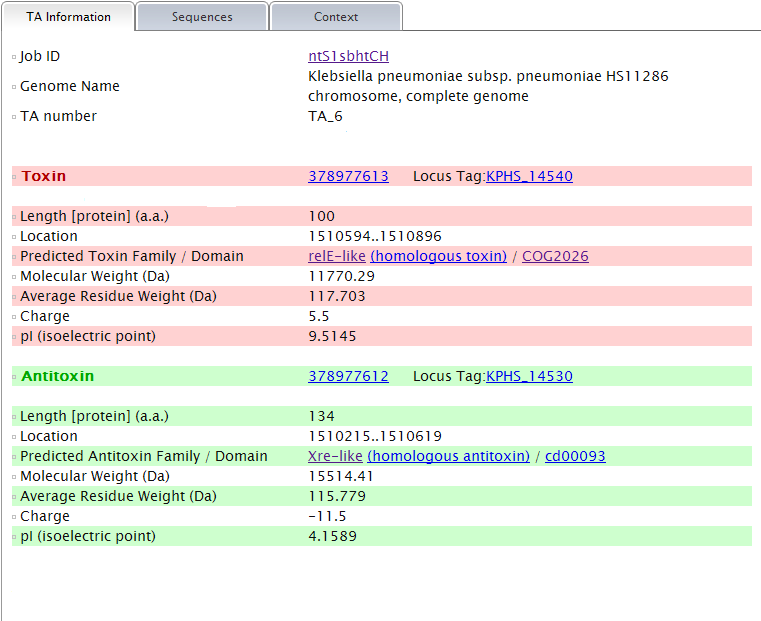 (2) Protein sequences of both predicted toxin and antitoxin are shown under the "Sequence" tab. Nucleotide sequences will be available based on proper input. A primer design tool is integrated to make it more convenient for your lab work. 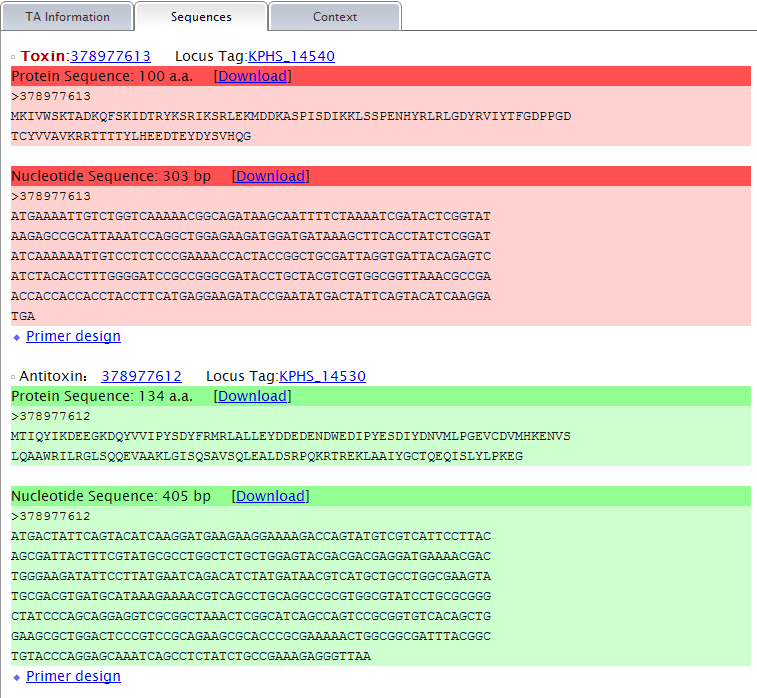 |
|
| Compare--distribution analysis of TA loci among other species. [TOP] | |
|
"Compare" provides you a solution to view the distribution of all the predicted TA loci among various genomes, which you may be interested in. By this, it is possible to figure out the conserved TA loci and the specific.
Note: (1) Input your subject genome (s) by accession number. A genome list is provided as reference. (2) You can set parameters for TA loci searching in subject genomes. 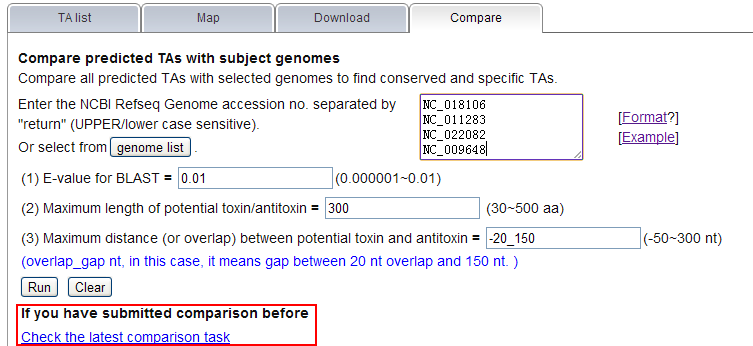 (3) Comparison is running 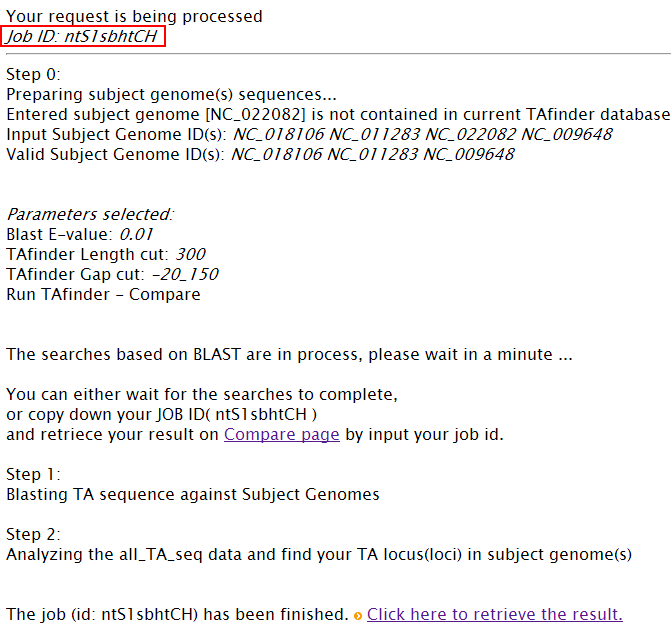 (4)You can define the rule to get conserved or specific results.  More details about H-value in rule1 please see More about parameter: what is H-value?   (5) All results are listed on this page, and you can download them in excel format as well. The name of each locus is a hyperlink, which allows all hits matching this TA locus from subject genomes to be shown, after you click it.   |
|
| Context--GI ( Genomic Island) related elements analysis in TA context. [TOP] | |
|
"Context" provides you a solution to analyze the TA loci contexts. It can profile most known bacterial virulence factors, resistance determinants, type III/IV/VI secretion system gene clusters and other mobile genetic elements (MGE).
Note: (1) You can set the range of TA locus context to be aligned. (2) Choose datasets for alignment. (3) Set patameters. 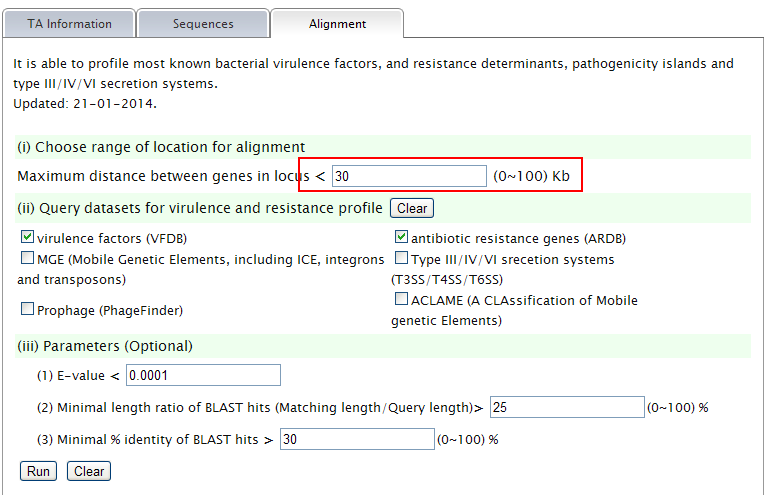 (4)The task is running. 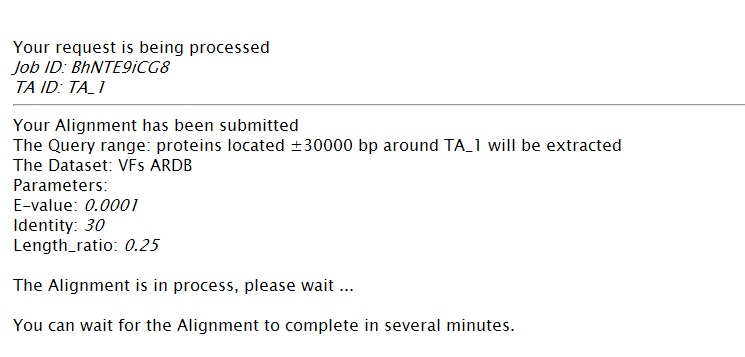 (5) TA locus context and hits will be listed. Predicted TA locus will be colored. An excel result will be provided as well. 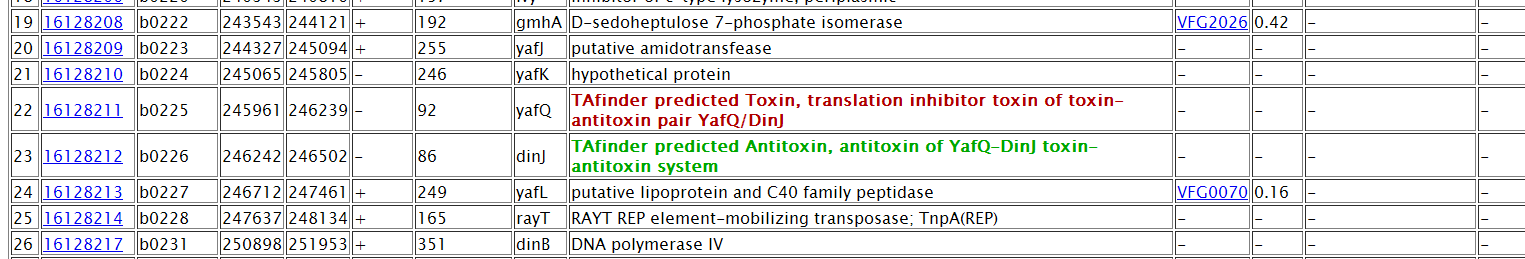 |
|
| More about parameter: what is H-value? [TOP] | |
|
TAfinder measures the protein sequence similarities by using BLASTp-based H-value. TAfinder uses H-value criteria which reflects the degree of protein sequence similarity in terms of the length of match and degree of identity between each query and subject while using BLASTp(Fukiya et al., 2004). BLASTp is used in TAfinder and its further analysis tools for protein sequence similarity analysis. Parameters such as e-value, Bit score and identity are usually used as filter values for analyzing its results. A normalized homology score (H-value) is calculated for each alignment result in turn. In this study, for each query protein, the H-value is calculated as follows: 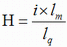
where is i the level of BLASTp identities of the region expressed as a frequency of between 0 and 100 (%), 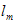 the length of matching sequence (including gaps), and the length of matching sequence (including gaps), and 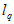 the query length. Therefore H belonged to the set, the query length. Therefore H belonged to the set, 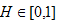 . . | |